In recent years, the world has been grappling with the COVID-19 pandemic, and understanding what a positive COVID test means is crucial for everyone. The virus, caused by the SARS-CoV-2, has affected millions of people globally, and being informed about testing, results, and next steps is vital for both personal health and public safety. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of positive COVID test results, their implications, and how to respond effectively.
1. What is a COVID Test?
Types of COVID Tests
There are two primary types of COVID tests used to diagnose the virus:
- PCR Tests: Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) tests are considered the gold standard for COVID-19 testing. They detect the virus’s genetic material and are known for their high accuracy. PCR tests are typically conducted using a nasal or throat swab and are analyzed in a laboratory.
- Antigen Tests: These tests detect specific proteins from the virus. Antigen tests are generally faster than PCR tests and can provide results in as little as 15 minutes. However, they may be less accurate, especially in individuals without symptoms or in the early stages of infection.
How COVID Tests Work
When you undergo a COVID test, a healthcare provider collects a sample (usually through a swab) from your nose or throat. This sample is then processed using either PCR or antigen testing methods. The results can be classified as positive, negative, or inconclusive.
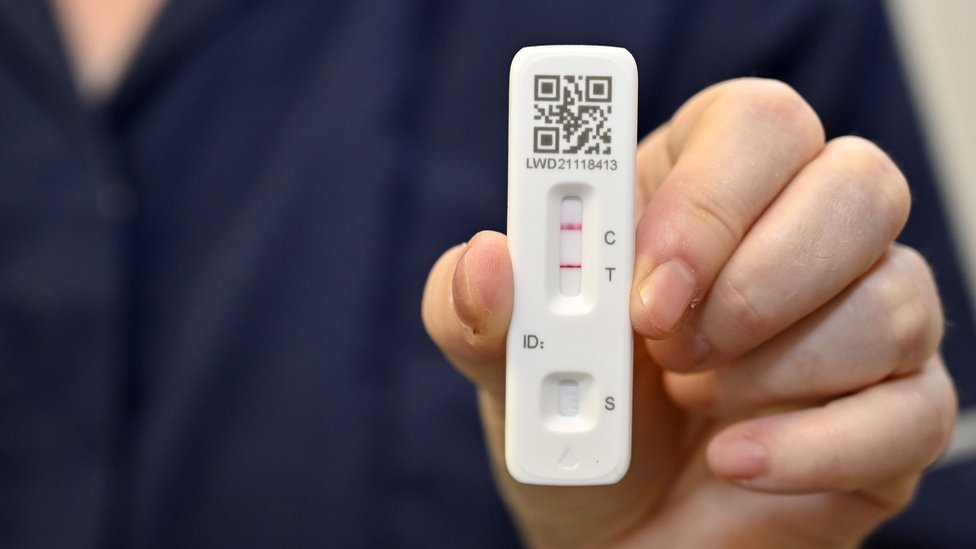
- Positive Test Result: Indicates that the virus is present in your body.
- Negative Test Result: Suggests that the virus was not detected at the time of testing.
- Inconclusive Result: Means the test could not determine if the virus was present; retesting may be needed.
Understanding these test types is essential in interpreting your health status and determining the next steps if you receive a positive COVID test result.
2. Understanding a Positive COVID Test Result
What Does It Mean?
Receiving a positive COVID test result means that the test has detected the presence of the virus in your body. This indicates that you are infected with COVID-19 and can potentially spread the virus to others. A positive result can occur regardless of whether you are experiencing symptoms or not.
It’s important to note that not all positive tests indicate an active infection. Some people may have lingering viral particles even after they have recovered from COVID-19. Therefore, it’s crucial to evaluate your symptoms and consult with healthcare professionals for guidance.
How Reliable Are COVID Tests?
The reliability of a COVID test depends on various factors, including the type of test used, the timing of the test, and how the sample was collected. Generally, PCR tests are more reliable than antigen tests. However, no test is perfect, and false positives or false negatives can occur.
- False Positive: This occurs when a test indicates that you have the virus when you do not. Factors contributing to false positives can include cross-reactivity with other viruses or errors in the testing process.
- False Negative: This happens when a test fails to detect the virus even though you are infected. False negatives are more common in antigen tests and may occur if the test is done too early or too late in the infection.
It is advisable to confirm a positive antigen test with a PCR test for more accurate results.
3. Symptoms of COVID-19
Common Symptoms
COVID-19 symptoms can vary widely from person to person. Some individuals may be asymptomatic, while others may experience severe symptoms. Common symptoms include:
- Fever or chills
- Cough
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Fatigue
- Muscle or body aches
- Loss of taste or smell
- Sore throat
- Congestion or runny nose
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
Severe Symptoms
In some cases, COVID-19 can lead to severe respiratory issues and other complications. Seek immediate medical attention if you or someone you know experiences:
- Difficulty breathing
- Persistent chest pain or pressure
- Confusion
- Inability to wake or stay awake
- Bluish lips or face
Recognizing these symptoms early can be critical in getting the necessary medical intervention.
4. What to Do After a Positive COVID Test
Isolation Guidelines
After receiving a positive COVID test result, it is crucial to isolate yourself to prevent spreading the virus to others. Here are the general isolation guidelines:
- Stay Home: Do not go to work, school, or public places.
- Isolate Yourself: Stay in a separate room away from other household members and pets as much as possible.
- Avoid Contact: Do not share personal items and limit interaction with others, even within your home.
- Follow Local Health Guidelines: Stay updated on your local health authority’s recommendations regarding isolation duration, as it may vary based on the latest findings.
Informing Close Contacts
It’s important to inform anyone you have been in close contact with (within 6 feet for more than 15 minutes) that you have tested positive for COVID-19. This enables them to monitor their symptoms and get tested if necessary.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you experience symptoms or have underlying health conditions, contact a healthcare provider for guidance. They can provide specific advice based on your situation, including whether you need further testing or treatment.
5. Treatment Options for COVID-19
Home Care
Most people with mild COVID-19 symptoms can recover at home without needing special treatment. Here are some tips for managing symptoms at home:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
- Rest: Give your body time to recover by getting adequate rest.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: You may take medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce fever and relieve body aches. Always consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medication.
Medical Treatment
For individuals with more severe symptoms or those at high risk of complications, medical treatment may be necessary. Options include:
- Antiviral Medications: Drugs like Paxlovid can be prescribed to reduce the severity of COVID-19 in certain patients.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: These can help reduce the risk of severe illness when administered early in the course of the disease.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for advanced treatment, including supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation.
Always discuss treatment options with a healthcare provider to ensure the best care for your situation.
6. Preventing the Spread of COVID-19
Vaccination
Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent severe illness and complications from COVID-19. Vaccines help your immune system recognize and fight the virus if exposed. It is recommended to:
- Get vaccinated as soon as you are eligible.
- Stay updated on booster shots, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are over a certain age.
Safety Measures
In addition to vaccination, following safety measures can help reduce the spread of COVID-19:
- Wear Masks: In crowded or indoor settings, wearing a mask can help protect yourself and others.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water or use hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
- Maintain Social Distancing: Keep a safe distance from others, especially in crowded places.
- Avoid Crowded Spaces: Limit time spent in large gatherings where the virus may spread easily.
Being proactive about these measures can significantly decrease the risk of infection.
7. Living with Long COVID
What is Long COVID?
Long COVID, also known as post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), refers to a range of symptoms that can persist for weeks or months after the initial COVID-19 infection has resolved. Symptoms can vary and may include:
- Fatigue
- Brain fog
- Joint pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Heart palpitations
Managing Long COVID Symptoms
If you experience symptoms of long COVID, it is essential to seek medical advice. Treatment may involve:
- Rehabilitation Programs: Tailored programs can help you regain strength and endurance.
- Symptom Management: Your healthcare provider can recommend strategies for managing persistent symptoms.
- Mental Health Support: Counseling or therapy can help address emotional and psychological challenges associated with long COVID.
Conclusion
The journey through the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of understanding what it means to receive a positive COVID test result. By being informed about testing, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their communities.
Staying informed is crucial for making the best decisions for your health and the health of those around you. As the situation continues to evolve, it is essential to rely on trusted sources and follow local health guidelines to navigate this challenging time effectively. By doing so, we can work together to reduce the
spread of the virus and support one another in the recovery process.