Understanding the Mastoid Process: A Detailed Exploration
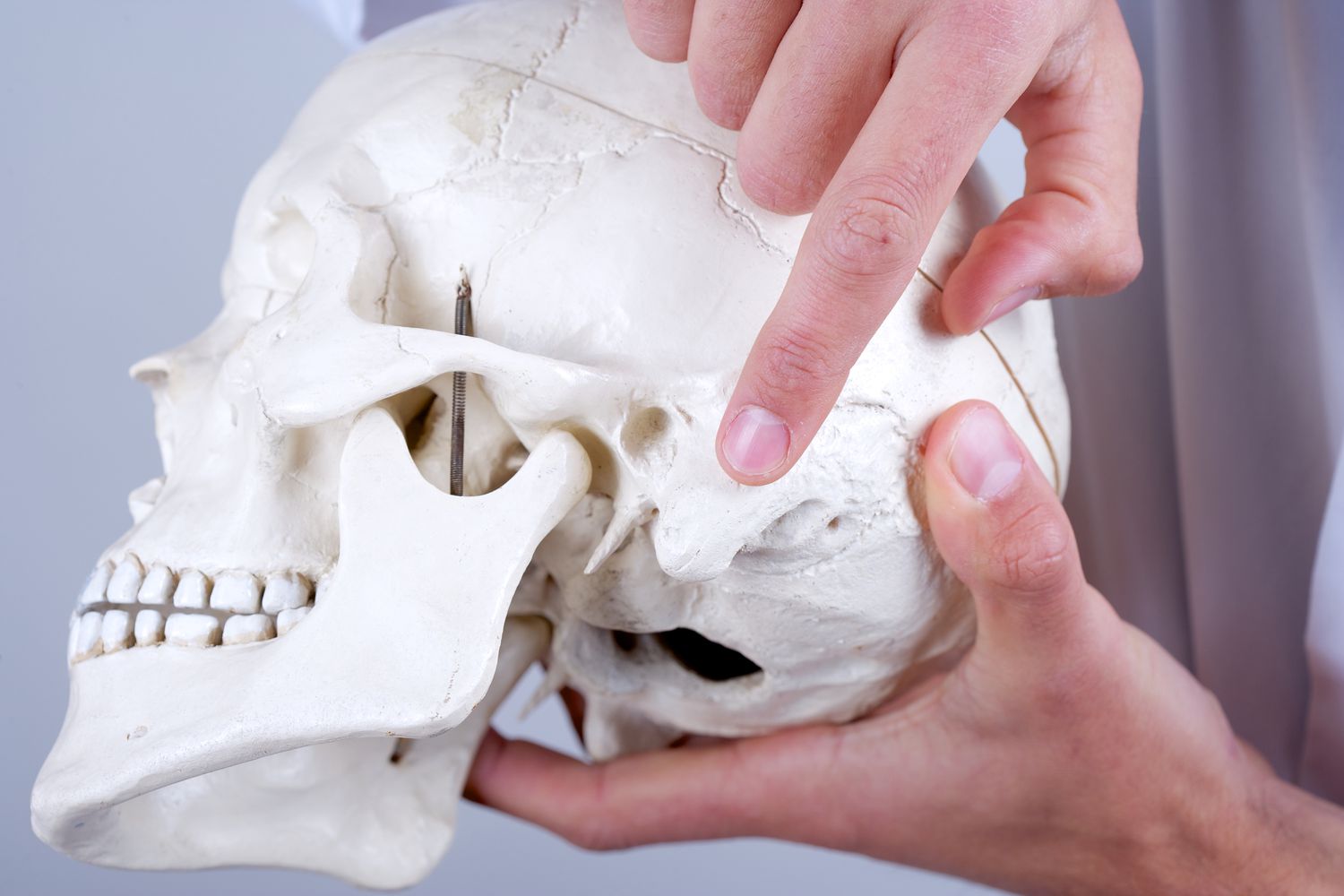
The mastoid process is a prominent bony structure located just behind the ear. It plays a vital role in the anatomy of the skull and has significant implications in medical science, particularly in relation to hearing, balance, and various diseases. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the mastoid process, discussing its anatomy, function, related conditions, and treatment options.
Anatomy of the Mastoid Process
1. Location and Structure
The mastoid process is part of the temporal bone, situated just behind the ear canal. It can be easily felt as a bony protrusion behind the ear. The process is shaped like a pyramid, with its base facing the skull and its apex pointing towards the neck. It consists of air-filled spaces, known as mastoid cells, which are connected to the middle ear. This structure is important for various functions, including the ear’s balance and hearing capabilities.
2. Relation to Other Anatomical Structures
The mastoid process is closely related to several important structures in the head and neck. It is located near the following:
- External Auditory Canal: The ear canal, through which sound waves travel to the eardrum.
- Middle Ear: The space behind the eardrum containing the ossicles, which are tiny bones essential for hearing.
- Inner Ear: Responsible for balance and hearing, the inner ear consists of the cochlea and vestibular system.
- Facial Nerve: This nerve runs close to the mastoid process, controlling muscles of facial expression.
- Jugular Vein: Located beneath the mastoid process, the jugular vein is responsible for draining blood from the head and neck.
Understanding the anatomical relationships is crucial for healthcare providers, especially during surgical procedures involving the ear and surrounding areas.
Function of the Mastoid Process
1. Sound Transmission and Balance
The mastoid process contributes to the overall function of the ear in two significant ways: sound transmission and balance. The mastoid air cells help to equalize pressure in the middle ear, facilitating optimal sound transmission. Additionally, the inner ear, which is connected to the mastoid process, is essential for maintaining balance and spatial orientation.
2. Muscle Attachment
The mastoid process serves as an attachment point for several muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid muscle. This muscle is responsible for turning and tilting the head. The attachment points for muscles provide the mastoid process with functional significance, influencing head movements and posture.
3. Air Reservoir
The mastoid air cells act as a reservoir of air, which helps maintain air pressure in the middle ear. This function is crucial, especially during activities like swallowing and yawning, which can create pressure changes in the ear.
Conditions Associated with the Mastoid Process
Several medical conditions can affect the mastoid process, leading to various symptoms and complications. Here are some of the most common conditions:
1. Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is an infection of the mastoid air cells, usually resulting from untreated middle ear infections (otitis media). Symptoms may include:
- Pain and swelling behind the ear
- Fever
- Hearing loss
- Discharge from the ear
Mastoiditis can lead to severe complications if left untreated, such as abscess formation or meningitis. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, and in some cases, surgery may be necessary to drain infected fluid.
2. Cholesteatoma
A cholesteatoma is an abnormal skin growth that can develop in the middle ear and mastoid process. It often arises due to repeated ear infections. Symptoms include:
- Persistent ear discharge
- Hearing loss
- A feeling of fullness in the ear
- Pain in the ear
If untreated, a cholesteatoma can erode bone, including the mastoid process, leading to further complications. Treatment often involves surgical removal of the growth.
3. Trauma and Fractures
Fractures of the mastoid process can occur due to trauma to the head, such as falls or accidents. Symptoms may include:
- Pain and swelling
- Hearing loss
- Bruising around the ear
In cases of fracture, medical evaluation is crucial to assess for associated injuries and determine appropriate treatment.
4. Tumors
Although rare, tumors can develop in the mastoid process, including both benign and malignant types. Symptoms may vary depending on the tumor’s size and location but can include:
- Persistent ear pain
- Hearing loss
- Swelling behind the ear
Diagnosis typically involves imaging studies such as CT scans or MRIs, and treatment may require surgery and other modalities depending on the tumor type.
Diagnosis of Mastoid Process Conditions
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history is essential for diagnosing conditions related to the mastoid process. Healthcare providers will ask about symptoms, medical history, and any prior ear infections. A physical examination may involve inspecting the ear and surrounding areas for swelling, redness, or discharge.
2. Imaging Studies
Imaging studies play a crucial role in diagnosing conditions affecting the mastoid process. Common imaging techniques include:
- X-rays: Useful for detecting fractures or bone abnormalities.
- CT Scans: Provide detailed images of the mastoid process and surrounding structures, helping to identify infections, tumors, or cholesteatomas.
- MRI: Useful for evaluating soft tissue and detecting tumors.
3. Audiological Assessment
Hearing tests may be conducted to assess the impact of mastoid process conditions on hearing function. These tests can help determine the extent of hearing loss and guide treatment options.
Treatment Options for Mastoid Process Conditions
1. Medications
In cases of infections like mastoiditis, antibiotics are the primary treatment. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort. In chronic conditions such as cholesteatoma, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms, but surgery is often required for definitive treatment.
2. Surgical Interventions
Surgical procedures may be necessary for more severe conditions affecting the mastoid process. Common surgical interventions include:
- Mastoidectomy: This procedure involves the removal of infected mastoid air cells to treat mastoiditis or cholesteatoma.
- Tympanoplasty: This surgery repairs the eardrum and middle ear structures, often performed in conjunction with mastoidectomy.
- Tympanomastoid Surgery: This combined approach addresses both the eardrum and mastoid process to treat chronic infections or growths.
3. Rehabilitation
After surgery or treatment for mastoid-related conditions, rehabilitation may be necessary to restore hearing and balance. This may include:
- Hearing Aids: If hearing loss persists, hearing aids can help improve auditory function.
- Vestibular Rehabilitation: Physical therapy may be recommended for individuals experiencing balance issues.
Preventive Measures for Mastoid Process Health
1. Ear Care
Maintaining good ear hygiene can help prevent infections that may affect the mastoid process. Some tips include:
- Avoid Inserting Objects in the Ear: This can cause trauma or push wax deeper into the ear canal.
- Treat Ear Infections Promptly: Seek medical attention for persistent ear infections to prevent complications.
- Avoid Water in the Ears: During swimming or bathing, use earplugs to prevent water from entering the ear canal.
2. Regular Check-ups
Regular visits to an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist can help monitor ear health, especially for individuals with a history of ear infections or related issues. Early detection of any problems can lead to more effective treatment.
3. Vaccinations
Vaccinations, such as the flu vaccine and pneumococcal vaccine, can help prevent respiratory infections that may lead to ear infections. Discuss vaccination options with a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
The mastoid process is a vital structure in the anatomy of the ear, playing an essential role in hearing, balance, and overall ear health. Understanding its anatomy, function, and associated conditions can help individuals recognize the importance of maintaining ear health and seeking appropriate medical care when needed.
With advancements in medical science and technology, many conditions affecting the mastoid process can be effectively diagnosed and treated, ensuring a better quality of life for those impacted by related issues. Regular check-ups and proper ear care can further aid in the prevention of complications, contributing to overall well-being.