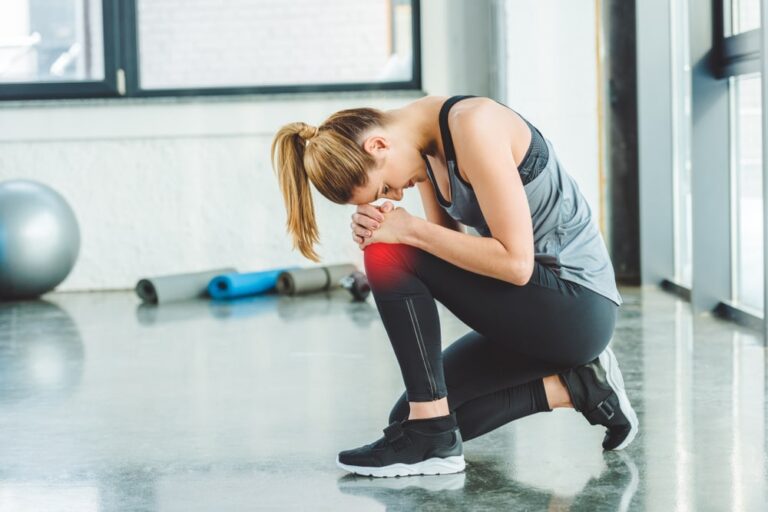
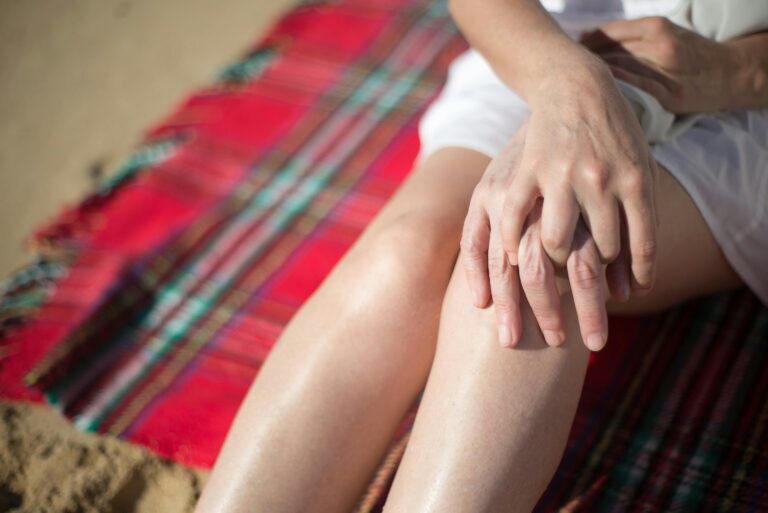
Pes anserine bursitis is a condition that affects the inner side of the knee, causing pain and discomfort. The term “pes anserine” refers to the area where three tendons attach to the shinbone (tibia). Bursitis, on the other hand, is the inflammation of a bursa, which is a small, fluid-filled sac that helps reduce friction between tissues. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures for pes anserine bursitis in detail.
What is Pes Anserine Bursitis?
Pes anserine bursitis occurs when the bursa located beneath the pes anserinus tendon becomes inflamed. The pes anserinus is formed by the tendons of three muscles: the sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus. These muscles originate from the pelvis and insert into the tibia, contributing to movements such as flexion and rotation of the knee.
Anatomy of the Pes Anserinus
To understand pes anserine bursitis, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the pes anserinus:
- Sartorius Muscle: This muscle runs down the front of the thigh and is responsible for hip flexion, knee flexion, and lateral rotation of the hip.
- Gracilis Muscle: Located in the inner thigh, the gracilis aids in hip adduction and knee flexion.
- Semitendinosus Muscle: Part of the hamstring group, this muscle also plays a role in knee flexion and hip extension.
These three tendons converge at the pes anserinus, creating a common attachment point on the tibia. When the bursa between these tendons and the bone becomes irritated, it leads to pes anserine bursitis.
Causes of Pes Anserine Bursitis
Pes anserine bursitis can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Overuse and Repetitive Activities
Engaging in activities that require repetitive knee movements, such as running, cycling, or jumping, can lead to overuse of the muscles attached to the pes anserinus. This repetitive strain can cause inflammation of the bursa.
2. Direct Trauma
Injuries to the knee area, such as falls or direct blows, can irritate the bursa and result in bursitis.
3. Obesity
Excess weight can put additional stress on the knee joints, increasing the risk of bursitis. The added pressure on the pes anserinus can lead to inflammation of the bursa.
4. Aging
As we age, the body’s ability to heal and recover from injuries decreases. This can lead to increased wear and tear on the bursa, making older adults more susceptible to pes anserine bursitis.
5. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as arthritis, diabetes, or gout, can increase the risk of developing pes anserine bursitis. These conditions can cause inflammation in the body, making the bursae more prone to irritation.
6. Improper Footwear
Wearing ill-fitting shoes or footwear that lacks proper support can affect walking and running mechanics. This can lead to abnormal stress on the knees and contribute to bursitis.
Symptoms of Pes Anserine Bursitis
Individuals with pes anserine bursitis may experience a variety of symptoms, including:
1. Pain and Tenderness
The primary symptom of pes anserine bursitis is pain on the inner side of the knee. The pain may worsen with activity, such as climbing stairs or running. Tenderness may also be felt when pressing on the pes anserinus area.
2. Swelling
Inflammation of the bursa can lead to localized swelling in the affected area. The swelling may be accompanied by warmth and redness.
3. Limited Range of Motion
Due to pain and swelling, individuals may experience difficulty bending or straightening the knee fully. This can affect daily activities and sports participation.
4. Stiffness
Stiffness in the knee joint, especially after periods of inactivity or upon waking in the morning, is a common symptom. This stiffness may improve with movement but can return after prolonged sitting or resting.
Diagnosing Pes Anserine Bursitis
A healthcare professional can diagnose pes anserine bursitis through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests.
1. Physical Examination
During the examination, the doctor will assess the knee for swelling, tenderness, and range of motion. They may also ask about the patient’s medical history, recent activities, and any previous knee injuries.
2. Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI may be ordered to rule out other conditions or to evaluate the extent of the inflammation. These tests can help visualize the bursa and the surrounding tissues.
Treatment Options for Pes Anserine Bursitis
Treatment for pes anserine bursitis typically involves a combination of conservative measures and, in some cases, medical interventions. The primary goals of treatment are to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and restore function.
1. Rest
Resting the affected knee is crucial in allowing the inflammation to subside. Avoiding activities that exacerbate pain can help promote healing.
2. Ice Therapy
Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time can help reduce swelling and numb the pain. This should be done several times a day, especially after activities.
3. Compression
Using a compression bandage or wrap can help minimize swelling and provide support to the knee. Be careful not to wrap it too tightly, as this can restrict blood flow.
4. Elevation
Elevating the knee while resting can help reduce swelling. Keeping the knee above the level of the heart allows excess fluid to drain away from the area.
5. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications or corticosteroid injections to control inflammation.
6. Physical Therapy
Once the acute pain and swelling subside, physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve flexibility. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to address specific weaknesses and imbalances.
7. Activity Modification
To prevent recurrence, individuals may need to modify their activities. This could involve adjusting running techniques, changing footwear, or incorporating cross-training activities that are less stressful on the knees.
8. Surgical Intervention
In rare cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be considered. This could involve removing the inflamed bursa or addressing any underlying structural issues contributing to the bursitis.
Preventing Pes Anserine Bursitis
Preventing pes anserine bursitis involves a combination of lifestyle changes and proper conditioning techniques. Here are some strategies to reduce the risk of developing this condition:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Keeping a healthy weight can help reduce stress on the knees. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can support weight management.
2. Use Proper Footwear
Wearing shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning can help improve biomechanics and reduce the risk of knee injuries. Custom orthotics may also be beneficial for individuals with specific foot issues.
3. Gradually Increase Activity Levels
When starting a new exercise program or returning after a break, it’s important to increase activity levels gradually. This helps the body adapt and reduces the risk of overuse injuries.
4. Incorporate Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the muscles around the knee, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles, can provide better support and stability to the joint. Focus on exercises that promote balanced muscle development.
5. Stretch Regularly
Incorporating stretching into your routine can improve flexibility and help prevent muscle tightness. Pay particular attention to the muscles around the hips and thighs.
6. Cross-Train
Engaging in a variety of physical activities can help reduce the risk of overuse injuries. Cross-training allows different muscle groups to be worked while giving specific muscles a break.
7. Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to any warning signs, such as pain or discomfort in the knees. If you experience any symptoms of pes anserine bursitis, take a break from activities that exacerbate the pain and seek medical advice if necessary.
Conclusion
Pes anserine bursitis is a painful condition that can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively. By adopting preventive measures and seeking timely treatment, individuals can reduce the risk of developing pes anserine bursitis and maintain healthy, pain-free knees. If you suspect you have this condition, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management plan.