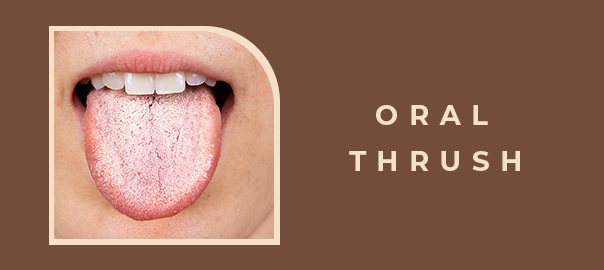
Oral thrush, a common fungal infection, affects millions of people, causing discomfort, pain, and difficulty swallowing. Characterized by white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and tonsils, oral thrush can be a persistent and frustrating condition. At our dental office in Livonia, we’ve seen firsthand the impact of oral thrush on our patients’ quality of life. Our experienced dentists and hygienists are dedicated to providing personalized care and effective treatment options to help manage oral thrush and prevent future occurrences.
In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for oral thrush, as well as provide valuable insights on maintaining good oral health and preventing this condition.
What Causes Oral Thrush?
Oral thrush occurs when there is an overgrowth of Candida albicans in the mouth. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including:
- Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to oral thrush.
- Antibiotics: Broad-spectrum antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the mouth, allowing Candida to overgrow.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can increase the risk of oral thrush.
- Diabetes: People with uncontrolled diabetes are more prone to oral thrush due to high blood sugar levels.
- Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly can contribute to the development of oral thrush.
What Are The Symptoms of Oral Thrush?
The symptoms of oral thrush can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- White patches: White, creamy patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and tonsils.
- Redness and inflammation: Redness, swelling, and inflammation of the affected areas.
- Pain and discomfort: Pain or discomfort when eating, drinking, or swallowing.
- Difficulty swallowing: Difficulty swallowing due to the presence of white patches or inflammation.
- Loss of taste: Altered sense of taste or metallic taste.
How is Oral Thrush Treated?
Treatment for oral thrush usually involves antifungal medications. These can be administered topically or systemically, depending on the severity of the infection. Common treatment options include:
- Clotrimazole: A topical antifungal medication available in the form of lozenges, tablets, or mouthwash.
- Nystatin: A topical antifungal medication available in the form of mouthwash or oral suspension.
- Fluconazole: A systemic antifungal medication available in the form of tablets or oral suspension.
- Natural remedies: Some natural remedies, such as probiotics, tea tree oil, and aloe vera, may also be effective in treating oral thrush.
What Are The Risk Factors?
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of developing oral thrush, including:
- Infants: Infants are more prone to oral thrush due to their immature immune systems.
- Older adults: Older adults are more susceptible to oral thrush due to age-related declines in immune function.
- People with HIV/AIDS: People with HIV/AIDS are more prone to oral thrush due to their compromised immune systems.
- People with cancer: People undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy are at a higher risk of developing oral thrush.
How is Oral Thrush Prevented?
Preventing oral thrush requires good oral hygiene practices, including:
- Brushing and flossing: Brushing and flossing regularly to remove bacteria and debris.
- Rinsing with mouthwash: Rinsing with an antifungal mouthwash to reduce the risk of oral thrush.
- Avoiding antibiotics: Avoid broad-spectrum antibiotics unless necessary.
- Managing stress: Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga.
Oral thrush is a common fungal infection that can be effectively treated with antifungal medications. However, it is essential to be aware of the risk factors and complications associated with this condition. By practicing good oral hygiene, avoiding antibiotics, and managing stress, individuals can reduce their risk of developing oral thrush. If symptoms persist or worsen, it is crucial to seek medical attention to prevent complications.