A glomus tumor is a rare type of tumor that originates from glomus cells, which are specialized smooth muscle cells primarily found in the skin, particularly in areas such as the fingertips and beneath the nails. Although glomus tumors are typically benign, they can cause significant discomfort and may lead to complications if not treated. This article will explore the various aspects of glomus tumors, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is a Glomus Tumor?
Definition and Characteristics
A glomus tumor is a type of neoplasm that arises from glomus bodies, which are responsible for regulating blood flow and temperature in the body. These tumors are most commonly found in the extremities, particularly in the fingers and toes, but can also occur in other areas of the body.
Glomus tumors are characterized by:
- Benign Nature: Most glomus tumors are non-cancerous and do not metastasize to other parts of the body.
- Painful Symptoms: Patients often experience severe pain, especially when pressure is applied to the tumor site.
- Small Size: These tumors are usually small, often measuring just a few millimeters in diameter.
Causes of Glomus Tumors
Genetic Factors
While the exact cause of glomus tumors is not well understood, there are some genetic factors that may play a role. Some patients may have a familial predisposition to developing glomus tumors, particularly those with conditions like multiple glomus tumors.
Environmental Factors
Certain environmental factors, such as repetitive trauma or injury to the fingers and toes, may increase the risk of developing glomus tumors. However, more research is needed to establish a direct link between environmental factors and the development of these tumors.
Symptoms of Glomus Tumors
Pain and Discomfort
The hallmark symptom of a glomus tumor is pain, which can be described as sharp, throbbing, or aching. The pain may worsen with temperature changes or pressure on the affected area.
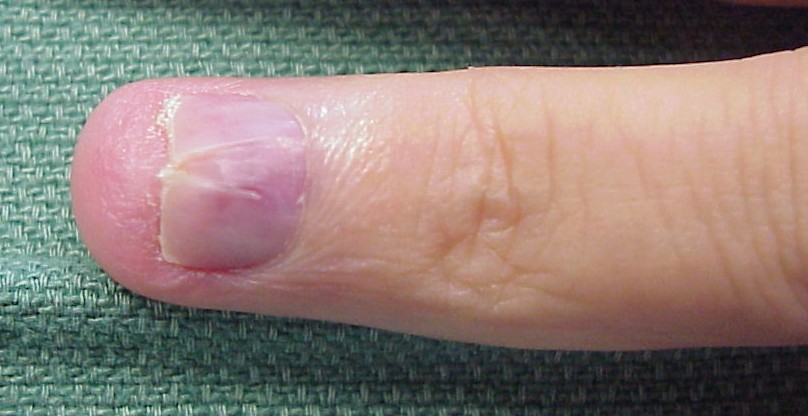
Color and Appearance
Glomus tumors may appear as small, blue, or red nodules under the skin. They can also be mistaken for other skin lesions or cysts. For more related articles, visit Healthline Media.
Sensitivity to Temperature
Patients with a glomus tumor may experience increased sensitivity to cold temperatures. This sensitivity can lead to further discomfort and may exacerbate the pain associated with the tumor.
Diagnosis of Glomus Tumors
Clinical Evaluation
Diagnosing a glomus tumor typically begins with a thorough clinical evaluation. A healthcare professional will assess the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and perform a physical examination to identify any unusual growths or lesions.
Imaging Studies
To confirm the diagnosis, imaging studies such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be utilized. These imaging techniques help visualize the tumor’s size and location, providing essential information for treatment planning.
Biopsy
In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. This involves removing a small sample of tissue from the tumor for laboratory analysis. The histological examination will help determine whether the tumor is indeed a glomus tumor and rule out other possible conditions.
Treatment Options for Glomus Tumors
Surgical Removal
The primary treatment for a glomus tumor is surgical excision. This involves removing the tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete removal. Surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia, and most patients can go home the same day.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: In some cases, minimally invasive techniques such as endoscopic surgery may be utilized to remove the tumor. This can lead to reduced recovery time and less postoperative pain.
Observation
In certain instances where the glomus tumor is asymptomatic or causing minimal discomfort, a healthcare provider may recommend a watchful waiting approach. Regular monitoring will help ensure that the tumor does not grow or cause additional problems.
Pain Management
For patients experiencing severe pain due to a glomus tumor, pain management strategies may be employed. This can include the use of over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription medications, or alternative therapies such as physical therapy.
Potential Complications of Glomus Tumors
Recurrence
Although glomus tumors are generally benign, they can recur after surgical removal. Patients should remain vigilant for any signs of recurrence, including new or worsening symptoms in the same area.
Nerve Damage
In rare cases, surgical removal of a glomus tumor may result in nerve damage, leading to numbness or tingling in the affected area. This risk can be minimized by selecting an experienced surgeon familiar with the delicate anatomy surrounding glomus tumors.
Infection
As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the site of the incision. Patients should follow postoperative care instructions carefully to reduce the likelihood of infection.
Living with a Glomus Tumor
Coping Strategies
Living with a glomus tumor can be challenging, especially for those experiencing pain and discomfort. Patients may benefit from the following coping strategies:
- Support Networks: Connecting with support groups or communities of individuals with similar experiences can provide emotional support and valuable resources.
- Education: Learning about glomus tumors and treatment options can empower patients and help them make informed decisions regarding their care.
Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring the patient’s condition and ensuring any potential complications are addressed promptly. These appointments may include physical examinations and imaging studies to check for any signs of recurrence.
Conclusion
A glomus tumor is a rare yet painful condition that can significantly affect a person’s quality of life. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help alleviate discomfort and prevent complications. If you suspect you may have a glomus tumor, seek medical attention promptly to explore your options for diagnosis and treatment.
Additional Resources
- Medical Associations: Many medical associations provide resources and support for patients with rare tumors.
- Patient Advocacy Groups: These organizations can offer valuable information and community support for individuals affected by glomus tumors.
By staying informed and proactive about your health, you can navigate the challenges posed by glomus tumors and maintain a fulfilling life.