Understanding Fondaparinux: A Comprehensive Guide
Fondaparinux is an anticoagulant medication widely used to prevent and treat blood clots. It belongs to a class of drugs known as factor Xa inhibitors, which work by blocking a specific protein in the blood clotting process. This article will explore fondaparinux in detail, including its mechanisms of action, uses, dosage, side effects, and more. We aim to provide a clear and thorough understanding of fondaparinux for readers who may not be familiar with medical terminology.
What is Fondaparinux?
Fondaparinux is a synthetic anticoagulant that is used to prevent and treat thrombosis (the formation of blood clots). It is often prescribed to patients undergoing surgery, those with certain medical conditions, or individuals at risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
How Does Fondaparinux Work?
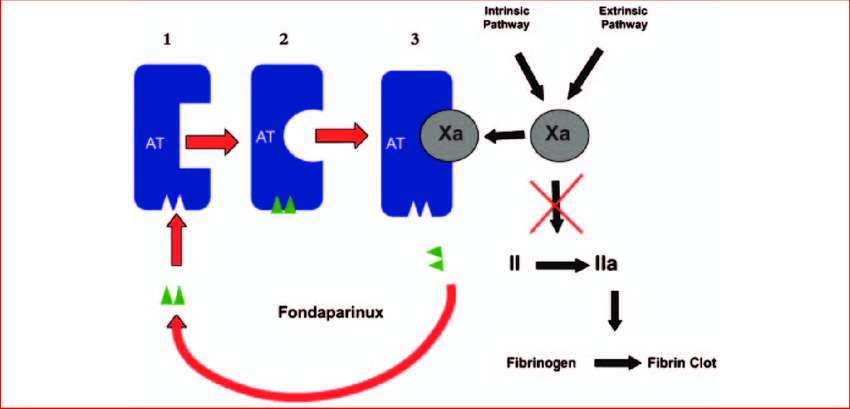
Fondaparinux works by inhibiting factor Xa, an essential component in the coagulation cascade, which is the series of steps that lead to blood clot formation. By blocking factor Xa, fondaparinux reduces the formation of thrombin, another protein critical for clot formation, thereby decreasing the ability of the blood to clot.
Mechanism of Action
- Binding to Antithrombin: Fondaparinux binds to a protein called antithrombin, which is responsible for inhibiting several enzymes in the clotting process, including factor Xa.
- Inhibition of Factor Xa: Once fondaparinux is bound to antithrombin, it enhances the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor Xa, leading to a decrease in thrombin generation.
- Prevention of Clot Formation: By inhibiting factor Xa, fondaparinux helps to prevent the formation of blood clots in the veins, making it effective in treating conditions like DVT and PE.
Uses of Fondaparinux
Fondaparinux is prescribed for various medical conditions. Here are some of the primary uses:
1. Prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Fondaparinux is commonly used to prevent DVT in patients undergoing major orthopedic or abdominal surgeries. DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the legs, which can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly.
2. Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
In addition to prevention, fondaparinux is also used to treat existing DVT and PE. By inhibiting clot formation, it helps to reduce the size of existing clots and prevent new ones from forming.
3. Unstable Angina and Myocardial Infarction
Fondaparinux may also be used in patients with unstable angina (chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart) or those experiencing a myocardial infarction (heart attack). In these situations, fondaparinux helps to prevent further clotting and supports better blood flow to the heart.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of fondaparinux varies based on the condition being treated and the patient’s individual characteristics. It is typically administered as a subcutaneous injection (under the skin). Here are general guidelines for dosage:
Adult Dosing for DVT Prophylaxis
- After Surgery: The usual dose is 2.5 mg once daily, starting 6 to 8 hours after surgery.
- Duration: Treatment usually continues for 5 to 9 days, depending on the type of surgery and the patient’s risk factors.
Adult Dosing for DVT/PE Treatment
- Initial Treatment: The recommended dose is 5 mg, 7.5 mg, or 10 mg once daily, depending on the patient’s weight and clinical condition.
- Duration: Treatment typically lasts for at least 5 days and may continue for several weeks or longer.
Special Considerations
- Renal Impairment: Dosage adjustments may be necessary for patients with renal impairment, as fondaparinux is primarily eliminated through the kidneys.
- Weight Considerations: The dosage may also vary based on the patient’s weight, particularly in the treatment of DVT and PE.
Side Effects of Fondaparinux
Like all medications, fondaparinux can cause side effects. While many patients tolerate it well, it is essential to be aware of potential adverse effects.
Common Side Effects
- Bleeding: Since fondaparinux is an anticoagulant, the most common side effect is bleeding. Patients should be monitored for any signs of unusual bleeding, such as:
- Blood in urine or stool
- Easy bruising
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts
- Anemia: Some patients may experience a decrease in red blood cells, leading to anemia. Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, and pale skin.
- Injection Site Reactions: Patients may experience pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site.
Serious Side Effects
- Severe Bleeding: In rare cases, fondaparinux can cause severe bleeding complications, which may require emergency medical attention. Symptoms may include:
- Sudden severe headache
- Sudden weakness or numbness
- Chest pain or difficulty breathing
- Thrombocytopenia: Fondaparinux can cause a decrease in platelets (thrombocytopenia), which can increase the risk of bleeding. Regular blood tests may be required to monitor platelet levels.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some patients may experience allergic reactions to fondaparinux, including rash, itching, or difficulty breathing.
Precautions and Contraindications
Before starting treatment with fondaparinux, patients should inform their healthcare provider of their medical history, particularly:
1. Bleeding Disorders
Patients with a history of bleeding disorders or active bleeding should use fondaparinux with caution, as it may exacerbate these conditions.
2. Renal Impairment
Fondaparinux is primarily eliminated by the kidneys, so caution is warranted in patients with renal impairment. Dosage adjustments may be necessary.
3. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Fondaparinux is classified as a Category B medication for pregnancy, meaning it is generally considered safe. However, pregnant women should discuss the risks and benefits with their healthcare provider. Fondaparinux is also excreted in breast milk, so nursing mothers should consult their doctors.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Patients receiving fondaparinux should have regular follow-up appointments to monitor their condition and response to treatment. Key aspects of monitoring include:
1. Blood Tests
Regular blood tests may be necessary to check:
- Platelet levels (to monitor for thrombocytopenia)
- Kidney function (to assess renal clearance of the drug)
- Hemoglobin and hematocrit (to monitor for anemia)
2. Clinical Monitoring
Patients should be monitored for signs of bleeding or other adverse effects. Any unusual symptoms should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately.
3. Adjustments in Therapy
Based on monitoring results, adjustments to the fondaparinux dosage may be required to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Interactions with Other Medications
Fondaparinux can interact with other medications, potentially increasing the risk of bleeding. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of all medications they are taking, including:
1. Other Anticoagulants
Using fondaparinux with other anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin, heparin) may increase the risk of bleeding.
2. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and aspirin, can also increase bleeding risk when taken with fondaparinux.
3. Certain Antibiotics
Some antibiotics, particularly those affecting liver enzymes, may interact with fondaparinux and require dosage adjustments.
Patient Education
Patients starting treatment with fondaparinux should receive thorough education on the medication, its uses, potential side effects, and the importance of adherence to therapy. Key points to discuss include:
1. Injection Technique
Patients should be instructed on the proper technique for self-administration of fondaparinux. This includes guidance on:
- Choosing an injection site (usually the abdomen or thigh)
- Rotating injection sites to avoid irritation
2. Recognizing Side Effects
Patients should be educated on the signs and symptoms of potential side effects, particularly unusual bleeding or allergic reactions. They should know when to seek immediate medical attention.
3. Importance of Follow-Up
Emphasizing the need for regular follow-up appointments and blood tests can help ensure effective monitoring and management of therapy.
Conclusion
Fondaparinux is a vital medication in the field of anticoagulation, offering effective prevention and treatment of blood clots. Its ability to inhibit factor Xa makes it a crucial option for patients at risk of DVT and PE. While fondaparinux is generally well-tolerated, awareness of potential side effects and interactions is essential for safe use. By understanding fondaparinux’s uses, dosage, side effects, and monitoring requirements, patients can work closely with their healthcare providers to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
In summary, fondaparinux is a critical tool in managing blood clotting disorders, and knowledge about this medication can empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare. If you have any further questions or concerns about fondaparinux, be sure to discuss them with your healthcare provider.