Acetic acid, also known as ethanoic acid, is a colorless liquid organic compound with a pungent smell and a sour taste. It is best known as the main component of vinegar, making it a staple in kitchens around the world. This article aims to explore the properties, production methods, applications, and significance of acetic acid in various fields.
What is Acetic Acid?
Definition and Chemical Structure
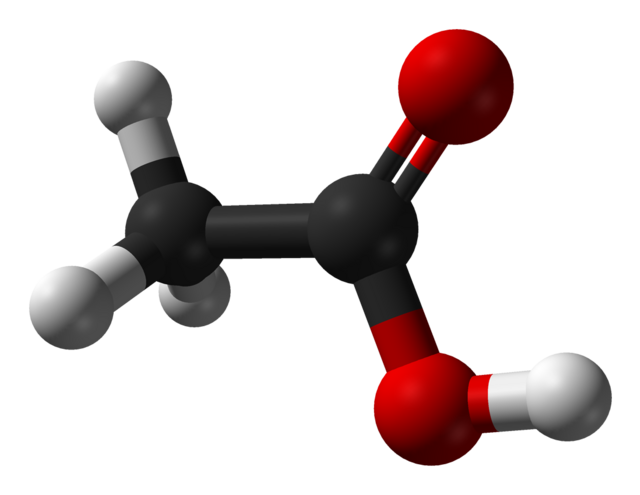
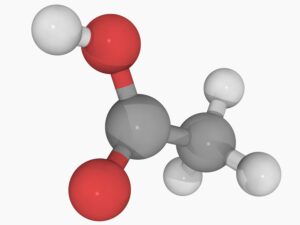
Acetic acid is a simple carboxylic acid with the chemical formula ( \text{C}_2\text{H}_4\text{O}_2 ) or ( \text{CH}_3\text{COOH} ). It consists of two carbon atoms, four hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. The molecule contains a carboxyl functional group ((-COOH)), which gives acetic acid its acidic properties. In its pure form, it is a colorless liquid that can be corrosive and has a characteristic sour odor.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Acetic acid has several distinctive physical and chemical properties:
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Odor: Pungent, vinegar-like smell
- Taste: Sour
- Density: 1.05 g/cm³ (more dense than water)
- Boiling Point: 118.1 °C (244.6 °F)
- Melting Point: 16.6 °C (61.88 °F)
Acetic acid is soluble in water, ethanol, and ether, making it a versatile solvent. It can react with bases to form salts (acetates) and can undergo esterification, a reaction with alcohols to form esters.
Historical Background
Acetic acid has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. It was first documented in ancient Egypt, where it was used in food preservation and as a flavoring agent. The term “vinegar” comes from the French word “vinaigre,” which means “sour wine.” In the Middle Ages, vinegar became an important commodity for culinary and medicinal purposes.
The industrial production of acetic acid began in the early 19th century, and significant advancements were made in the chemical synthesis processes. Today, acetic acid is produced on a large scale and is a crucial chemical in various industries.
Production of Acetic Acid
Natural Production
Acetic acid is produced naturally through the fermentation of sugars. Yeast and bacteria convert sugars into ethanol and acetic acid, respectively. This process is commonly used in vinegar production, where alcohol is oxidized into acetic acid by acetic acid bacteria.
Synthetic Production
Most acetic acid produced today is made through synthetic methods. The two primary methods of industrial production are:
1. Carbonylation of Methanol
This method involves the reaction of methanol with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst, usually rhodium or iridium. The reaction can be summarized as follows:
[
\text{CH}_3\text{OH} + \text{CO} \rightarrow \text{CH}_3\text{COOH}
]
This process is highly efficient and accounts for a significant portion of the world’s acetic acid production.
2. Oxidation of Ethylene
In this process, ethylene is oxidized using a catalyst, typically using air or oxygen, to produce acetic acid:
[
\text{C}_2\text{H}_4 + \text{O}_2 \rightarrow \text{CH}_3\text{COOH}
]
This method is less common than the carbonylation of methanol but still plays a role in acetic acid production.
Global Production and Demand
As of recent data, the global production of acetic acid exceeds 15 million metric tons per year, with the highest production rates found in countries such as China, the United States, and Germany. The demand for acetic acid is expected to grow due to its applications in various industries, including food and beverage, textiles, and plastics.
Uses of Acetic Acid
Acetic acid has a wide range of applications across various industries:
1. Food Industry
Acetic acid is primarily known for its role in food preservation and flavoring. It is a key ingredient in vinegar, which is used in salad dressings, marinades, and pickling. Its antimicrobial properties help inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, making it an effective preservative.
2. Industrial Applications
In industry, acetic acid is used as a chemical building block in the production of:
- Acetic Anhydride: Used in the production of plastics, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
- Vinyl Acetate: A key ingredient in adhesives, paints, and coatings.
- Acetates: Salts and esters of acetic acid are used in a variety of applications, including textiles, plastics, and food additives.
3. Pharmaceuticals
Acetic acid is used in the pharmaceutical industry for the synthesis of various drugs and medical compounds. Its ability to serve as a solvent and reactant makes it an essential chemical in drug formulation.
4. Cleaning and Household Products
Due to its antimicrobial properties, acetic acid is a common ingredient in cleaning products. It can be used to remove stains, odors, and mineral deposits, making it effective for household cleaning tasks.
5. Agriculture
In agriculture, acetic acid is used as a herbicide and fungicide. Its effectiveness in controlling weeds and pests makes it a valuable tool for farmers looking for eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic chemicals.
6. Laboratory Applications
Acetic acid is widely used in laboratories for various purposes, including as a solvent in chemical reactions, a reagent in titrations, and a medium for biological assays.
Health and Safety Considerations
Toxicity and Exposure
While acetic acid is safe for consumption in low concentrations (as found in vinegar), concentrated acetic acid can be corrosive and harmful. Prolonged exposure can cause skin burns, eye damage, and respiratory issues. It is essential to handle concentrated acetic acid with care, using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and masks.
Environmental Impact
Acetic acid is biodegradable and poses a low risk to the environment when used responsibly. However, large spills or releases can lead to soil and water contamination. It is crucial to follow proper disposal guidelines to minimize environmental impact.
Acetic Acid in Research and Development
Recent Advances
Research on acetic acid has expanded in recent years, focusing on its applications in renewable energy, bioplastics, and biotechnology. Scientists are exploring innovative ways to produce acetic acid using biomass and waste materials, which can lead to more sustainable production methods.
Acetic Acid in Biotechnology
In biotechnology, acetic acid is being investigated for its role in metabolic pathways and its potential as a biofuel. Understanding how microorganisms produce acetic acid can pave the way for more efficient biofuel production methods, potentially reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Conclusion
Acetic acid is a versatile and essential compound with numerous applications across various industries. From its role as a food preservative to its importance in chemical synthesis and biotechnology, acetic acid plays a crucial part in our daily lives and the global economy. As research continues to uncover new uses and production methods, acetic acid will likely remain a significant player in the chemical landscape for years to come.
Summary
In summary, this article has explored the following aspects of acetic acid:
- Definition and Chemical Structure: A simple carboxylic acid known for its sour taste and pungent smell.
- Production: Natural fermentation and synthetic methods such as carbonylation of methanol and oxidation of ethylene.
- Uses: Applications in food, industry, pharmaceuticals, cleaning, agriculture, and laboratories.
- Health and Safety: Importance of handling with care and awareness of environmental impacts.
- Research and Development: Advances in sustainable production and applications in biotechnology.
As we continue to explore the properties and uses of acetic acid, it remains a vital component of many aspects of our lives.