In the world of cooking and baking, ingredients play a crucial role in achieving the desired flavor, texture, and appearance of your dishes. One ingredient that has been a staple in many recipes is palm shortening. However, due to various reasons such as health concerns, environmental impacts, and dietary restrictions, many people are searching for a suitable substitute for palm shortening. This article will explore several alternatives to palm shortening, their uses, and how to choose the right one for your culinary needs.
Understanding Palm Shortening
What is Palm Shortening?
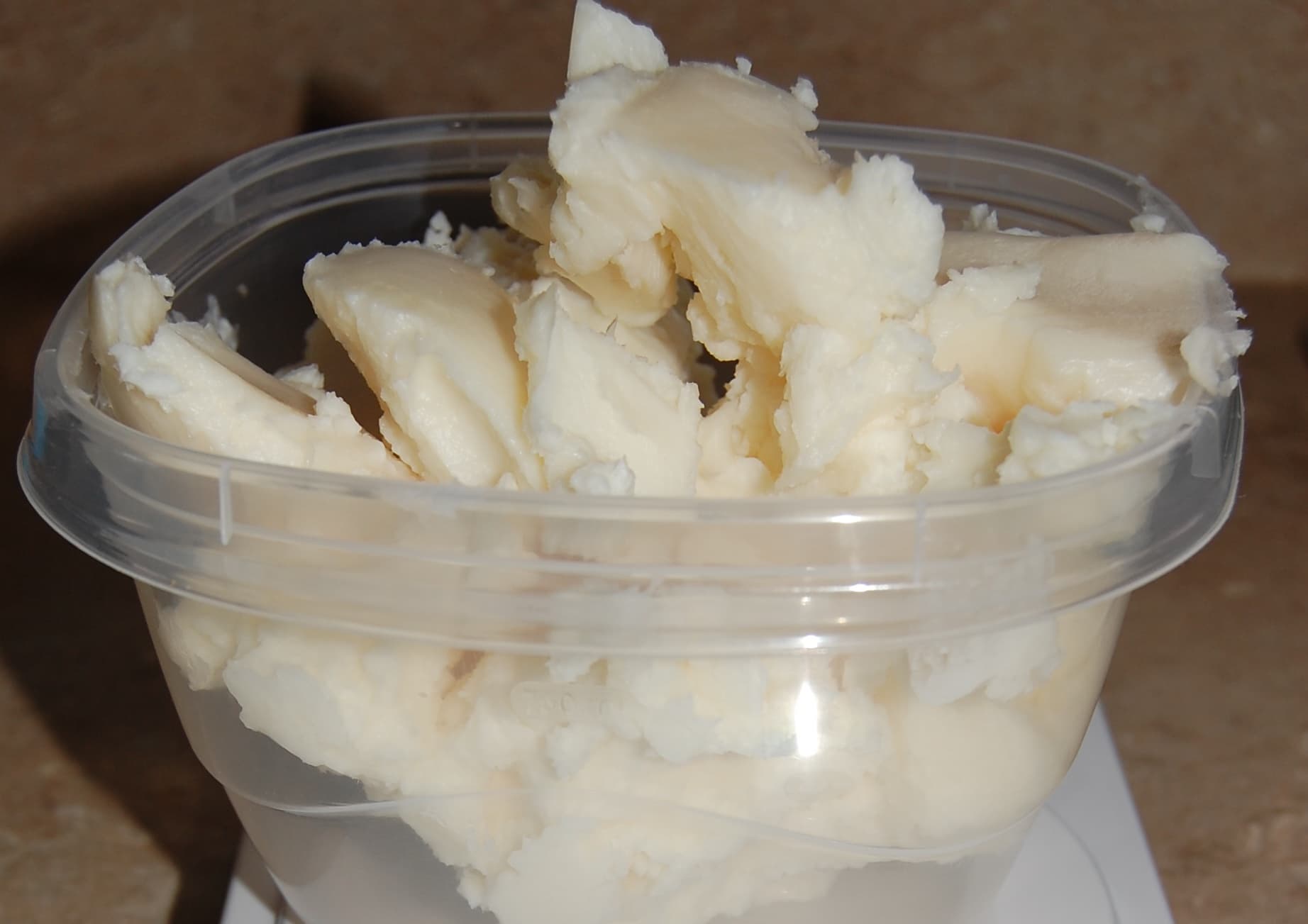
Palm shortening is a type of fat derived from the fruit of the oil palm tree. It is commonly used in baking and cooking due to its ability to create a light, fluffy texture in baked goods. Palm shortening is favored for its high melting point, which allows it to maintain its structure during baking, resulting in baked goods that hold their shape well.
Why Use Palm Shortening?
Palm shortening is often chosen for its creamy texture, neutral flavor, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It can replace butter or other fats in recipes, making it a versatile option in various dishes. Additionally, it is free from trans fats and is a popular choice among those looking for a non-dairy alternative.
Concerns About Palm Shortening
Despite its advantages, palm shortening has faced criticism for its environmental impact. The production of palm oil has been linked to deforestation, habitat destruction, and loss of biodiversity in regions like Southeast Asia. Furthermore, some people may have health concerns regarding the saturated fat content in palm shortening. As a result, many individuals are seeking substitutes that are more environmentally friendly and healthier.
The Need for Alternatives
Given the concerns surrounding palm shortening, it’s essential to explore alternatives that can provide similar benefits without the associated drawbacks. The search for a substitute for palm shortening is important for bakers and cooks who want to create delicious dishes while adhering to their dietary preferences and ethical considerations.
Top Substitutes for Palm Shortening
1. Coconut Oil
Overview
Coconut oil is a popular substitute for palm shortening due to its similar texture and fat content. Derived from the meat of coconuts, this oil is rich in medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) and has gained popularity for its health benefits.
Uses in Cooking and Baking
Coconut oil can be used in a 1:1 ratio as a replacement for palm shortening. It works well in baked goods like cookies, cakes, and muffins, providing a slightly tropical flavor. Additionally, coconut oil can be solid or liquid depending on the temperature, so it’s important to note the state when measuring for recipes.
Benefits
- Rich in healthy fats
- Can improve digestion
- Contains antimicrobial properties
Drawbacks
- Distinct coconut flavor may not suit all recipes
- Solid coconut oil can be harder to mix into batters compared to shortening
2. Butter
Overview
Butter is a classic alternative to palm shortening and offers a rich flavor and creamy texture. Made from churned cream, butter is a staple in many kitchens.
Uses in Cooking and Baking
You can substitute butter for palm shortening at a 1:1 ratio. However, because butter contains water, it may alter the texture of your baked goods slightly. To compensate, consider reducing other liquids in the recipe.
Benefits
- Adds rich flavor to baked goods
- Provides a tender texture
Drawbacks
- Not suitable for dairy-free or vegan diets
- Higher in saturated fat compared to some alternatives
3. Margarine
Overview
Margarine is a popular butter substitute made from vegetable oils. It comes in various forms, including stick and tub varieties.
Uses in Cooking and Baking
Margarine can be used as a direct replacement for palm shortening in recipes. However, check the label to ensure it is free from trans fats.
Benefits
- Can be a dairy-free option
- Versatile for various recipes
Drawbacks
- Often contains additives and preservatives
- May not provide the same flavor profile as butter or shortening
4. Vegetable Shortening
Overview
Vegetable shortening is made from hydrogenated vegetable oils and is similar to palm shortening in texture and function.
Uses in Cooking and Baking
Like palm shortening, vegetable shortening can be used in a 1:1 ratio. It is ideal for baked goods that require a flaky texture, such as pie crusts and biscuits.
Benefits
- Neutral flavor that won’t alter the taste of baked goods
- Great for achieving flakiness
Drawbacks
- May contain trans fats depending on the brand
- Lacks the flavor richness of butter
5. Applesauce
Overview
For those looking for a healthier option, unsweetened applesauce can serve as a substitute for palm shortening, especially in baked goods.
Uses in Cooking and Baking
Applesauce can replace palm shortening at a 1:1 ratio in recipes. However, it works best in moist baked goods like cakes and muffins rather than in recipes that require a flaky texture.
Benefits
- Low in calories and fat
- Adds natural sweetness and moisture to baked goods
Drawbacks
- Alters the flavor and texture of the final product
- Not suitable for savory dishes
6. Avocado
Overview
Avocado is a nutrient-dense fruit that can be mashed and used as a fat substitute in recipes.
Uses in Cooking and Baking
Mashed avocado can replace palm shortening in a 1:1 ratio, particularly in baked goods like brownies or cookies, adding moisture and healthy fats.
Benefits
- Rich in healthy monounsaturated fats
- High in vitamins and minerals
Drawbacks
- Distinct flavor may not suit all recipes
- Can alter the color of baked goods
7. Nut Butters
Overview
Nut butters, such as almond or cashew butter, can also serve as an alternative to palm shortening.
Uses in Cooking and Baking
Nut butters can replace palm shortening in a 1:1 ratio, adding a nutty flavor to cookies, bars, and other baked goods.
Benefits
- Provides healthy fats and protein
- Adds flavor and creaminess
Drawbacks
- Not suitable for those with nut allergies
- Alters the taste of the final product
Choosing the Right Substitute
When selecting a substitute for palm shortening, consider the following factors:
1. Recipe Type
Different recipes may require different substitutes. For instance, flaky pastries may benefit from using vegetable shortening, while moist cakes might work better with applesauce or coconut oil.
2. Dietary Restrictions
If you have specific dietary needs, such as vegan or gluten-free, ensure that your substitute aligns with those restrictions. Many of the options listed above cater to various dietary preferences.
3. Flavor Profile
Consider how the flavor of the substitute will affect your dish. For example, coconut oil will impart a coconut flavor, while butter will add a rich creaminess.
4. Health Considerations
Evaluate the nutritional content of your substitute. Some options, like applesauce or avocado, provide health benefits, while others may contain higher levels of saturated fats.
Conclusion
Finding a substitute for palm shortening can enhance your cooking and baking experience while aligning with your dietary preferences and environmental concerns. Whether you choose coconut oil, butter, margarine, or a fruit-based alternative, each option has its unique benefits and potential drawbacks. Experimenting with these substitutes can help you discover the best fit for your recipes and create delicious, satisfying dishes that everyone will enjoy.
As the culinary world continues to evolve, so does our understanding of ingredients and their impact on our health and the environment. By making informed choices, you can enjoy delicious meals while supporting a more sustainable future. So go ahead, explore these alternatives, and happy cooking!