Recommended Hours of Sleep: What You Need to Know for Optimal Health
Getting enough sleep is crucial for maintaining good health and well-being, but how many hours of sleep do you actually need? In this article, we’ll explore the recommended hours of sleep for different age groups, the benefits of adequate sleep, and tips for improving your sleep quality. Understanding these guidelines can help you make informed decisions about your sleep habits and ensure you’re getting the rest you need.
Understanding the Recommended Hours of Sleep
The Basics of Sleep Recommendations
When we talk about the recommended hours of sleep, we’re referring to the amount of sleep that experts suggest for different age groups to promote optimal health. These recommendations come from various health organizations, including the National Sleep Foundation and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). While individual sleep needs can vary, these guidelines provide a useful framework for understanding how much sleep most people need.
Age-Specific Sleep Recommendations
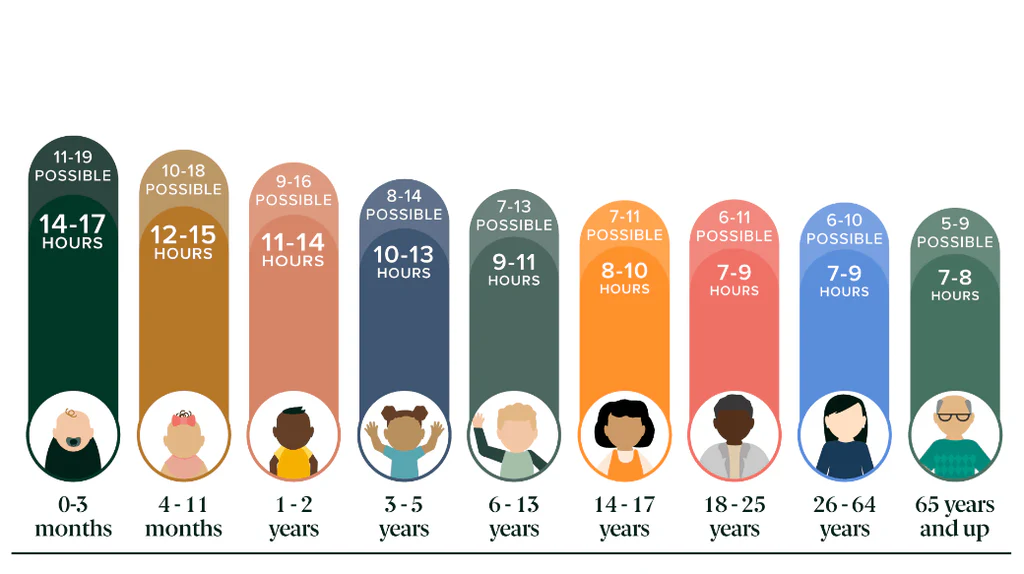
The amount of sleep you need changes throughout your life. Here’s a breakdown of the recommended hours of sleep for different age groups:
- Newborns (0-3 months): 14-17 hours per day
- Infants (4-11 months): 12-15 hours per day
- Toddlers (1-2 years): 11-14 hours per day
- Preschoolers (3-5 years): 10-13 hours per day
- School-Aged Children (6-13 years): 9-11 hours per day
- Teenagers (14-17 years): 8-10 hours per day
- Young Adults (18-25 years): 7-9 hours per night
- Adults (26-64 years): 7-9 hours per night
- Older Adults (65+ years): 7-8 hours per night
These recommendations are based on research indicating that these amounts are generally associated with the best overall health and functioning.
The Importance of Adequate Sleep
Physical Health Benefits
Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining physical health. Here are some key benefits:
- Immune System Support: Sleep helps regulate the immune system. A lack of sleep can impair the body’s ability to fight off illnesses and infections.
- Heart Health: Good sleep is linked to lower risks of heart disease and hypertension. Chronic sleep deprivation can increase the risk of cardiovascular problems.
- Weight Management: Sleep influences hormones that regulate hunger and appetite. Poor sleep can lead to weight gain and obesity.
- Cellular Repair: During sleep, the body repairs tissues and muscles, helping you recover from physical exertion and injury.
Mental and Emotional Well-being
Sleep also plays a crucial role in mental and emotional health:
- Cognitive Function: Adequate sleep improves memory, learning, and problem-solving skills. It also helps with focus and concentration.
- Emotional Regulation: Good sleep helps regulate emotions and reduces the risk of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
- Stress Reduction: Proper sleep can help manage stress and improve overall mental resilience.
Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
Short-Term Effects
Lack of sleep can have immediate effects on your body and mind, including:
- Decreased Alertness: Sleep deprivation can lead to reduced alertness and impaired reaction times, which can affect daily activities and safety.
- Cognitive Impairment: Short-term memory problems and difficulties with concentration are common when you’re not getting enough sleep.
- Mood Changes: Irritability and mood swings are frequent among those who don’t get enough rest.
Long-Term Health Risks
Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to more serious health issues over time:
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Long-term lack of sleep is associated with a higher risk of chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
- Mental Health Issues: Prolonged sleep deprivation can contribute to the development of mental health disorders like depression and anxiety.
- Decreased Lifespan: Research suggests that chronic sleep deprivation may be linked to a shorter lifespan.
Tips for Improving Sleep Quality
Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Your sleep environment can significantly impact your sleep quality:
- Comfortable Bedding: Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows to support restful sleep.
- Dark and Quiet: Use blackout curtains and white noise machines if necessary to create a conducive sleep environment.
- Cool Temperature: Maintain a cool room temperature to promote better sleep.
Establishing a Consistent Sleep Routine
Consistency is key for good sleep hygiene:
- Regular Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Bedtime Rituals: Develop a relaxing pre-sleep routine, such as reading or taking a warm bath, to signal your body that it’s time to wind down.
Managing Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle habits can impact your sleep:
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Avoid consuming caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime as they can interfere with sleep.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can promote better sleep, but try to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime.
- Avoid Screens Before Bed: Reduce exposure to screens at least an hour before bed to prevent blue light from disrupting your sleep.
Addressing Sleep Disorders
Common Sleep Disorders
Sometimes, despite following good sleep practices, you may still experience sleep problems. Common sleep disorders include:
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling or staying asleep.
- Sleep Apnea: Interrupted breathing during sleep.
- Restless Legs Syndrome: An uncomfortable urge to move the legs, especially at night.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you have persistent sleep issues that affect your daily life, consider consulting a healthcare professional. They can help diagnose any underlying sleep disorders and recommend appropriate treatments.
Conclusion
Understanding and adhering to the recommended hours of sleep for your age group is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. By following sleep guidelines, creating a restful sleep environment, and managing lifestyle factors, you can improve your sleep quality and, in turn, your quality of life. Remember, good sleep is not just about the number of hours you get, but also about the quality of those hours. Prioritize your sleep, and your body and mind will thank you.