HDL Cholesterol Low: Understanding the Causes, Risks, and Solutions
HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) cholesterol is often referred to as the “good” cholesterol due to its role in removing excess cholesterol from your bloodstream and transporting it to the liver for excretion. However, when your HDL cholesterol levels are low, it can pose significant risks to your cardiovascular health. This article will delve into the causes, risks, and strategies for managing low HDL cholesterol in easy-to-understand terms.
What is HDL Cholesterol?
The Role of HDL Cholesterol in Your Body
HDL cholesterol plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of cholesterol in your body. Unlike LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) cholesterol, which can lead to plaque buildup in your arteries, HDL cholesterol helps to remove excess cholesterol, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
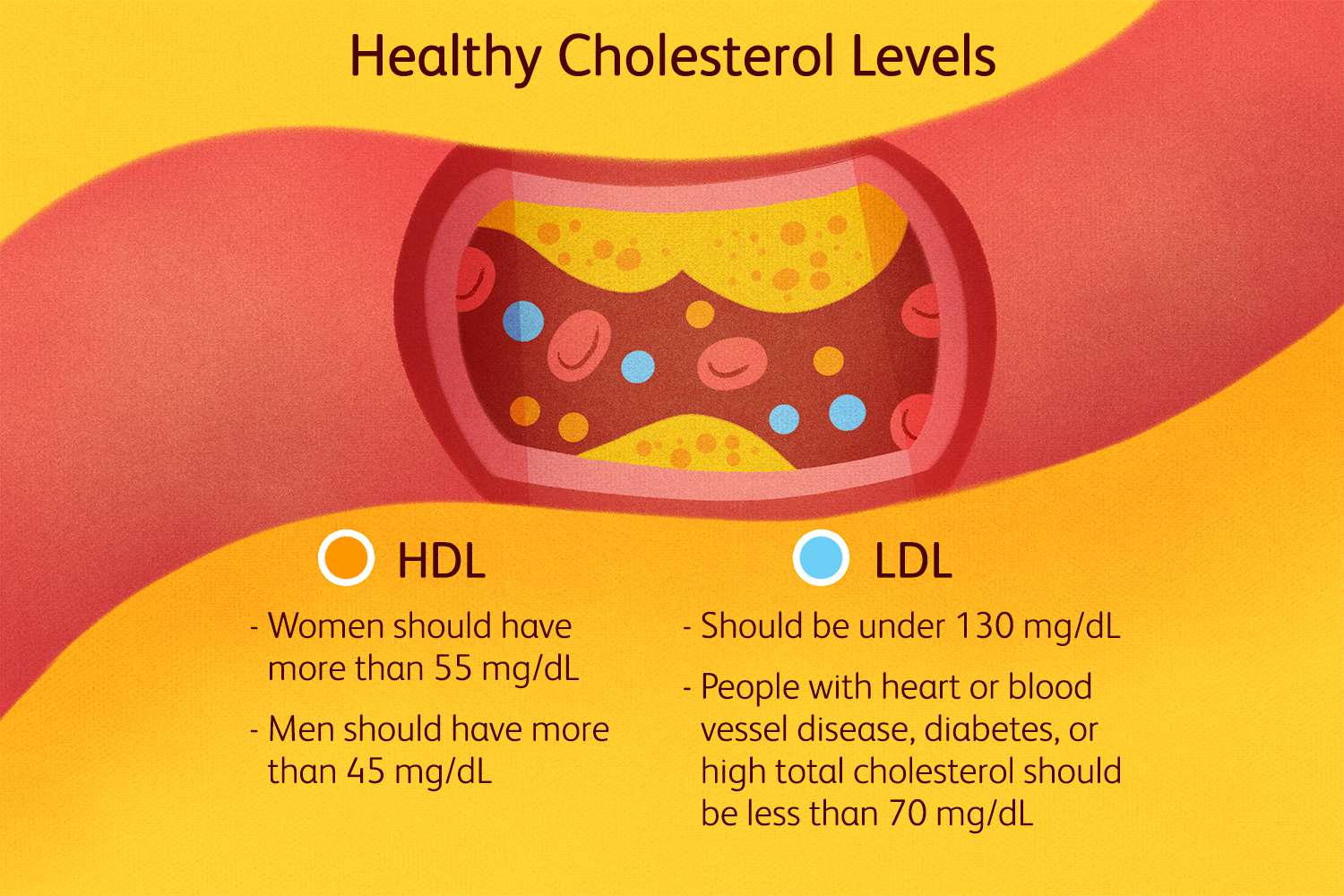
Understanding Cholesterol Levels
Cholesterol levels are typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) of blood. For HDL cholesterol, higher levels are generally better. An HDL cholesterol level of 60 mg/dL or higher is considered protective against heart disease, while a level below 40 mg/dL for men and 50 mg/dL for women is considered low, increasing the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Causes of Low HDL Cholesterol
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in determining your HDL cholesterol levels. If you have a family history of low HDL cholesterol, you may be more likely to experience the same issue.
Poor Diet
A diet high in refined carbohydrates, trans fats, and sugar can contribute to low HDL cholesterol levels. These dietary choices can increase triglycerides and lower HDL cholesterol, negatively impacting your heart health.
Lack of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity helps to raise HDL cholesterol levels. Sedentary lifestyles, on the other hand, can contribute to low HDL cholesterol. Exercise not only increases HDL cholesterol but also improves overall cardiovascular health.
Smoking
Smoking is a major factor that can lower HDL cholesterol levels. The chemicals in tobacco can damage blood vessels and reduce the ability of HDL cholesterol to perform its function of removing excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Obesity
Obesity, particularly abdominal obesity, is linked to lower HDL cholesterol levels. Excess body fat can increase triglycerides and lower HDL cholesterol, leading to an increased risk of heart disease.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and liver disease, can contribute to low HDL cholesterol levels. These conditions often involve insulin resistance, which is associated with lower HDL cholesterol and higher triglycerides.
Risks Associated with Low HDL Cholesterol
Increased Risk of Heart Disease
Low HDL cholesterol levels are strongly associated with an increased risk of heart disease. HDL cholesterol helps to clear LDL cholesterol from your arteries, reducing the risk of plaque buildup and heart attacks. More read here: Disadvantages of Eating R: An In-Depth Analysis
Stroke Risk
Just as low HDL cholesterol increases the risk of heart disease, it also raises the risk of stroke. Plaque buildup in the arteries can lead to blockages in the blood vessels supplying the brain, resulting in a stroke.
Other Cardiovascular Issues
Low HDL cholesterol levels are linked to other cardiovascular problems, such as peripheral artery disease (PAD) and atherosclerosis. These conditions can lead to reduced blood flow to the limbs and other parts of the body, causing pain and increasing the risk of complications.
Diagnosing Low HDL Cholesterol
Routine Blood Tests
Low HDL cholesterol is typically diagnosed through a routine blood test called a lipid panel or lipid profile. This test measures your total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Understanding Your Lipid Profile
When you receive your lipid profile results, your healthcare provider will look at your HDL cholesterol level in the context of your overall cholesterol levels and cardiovascular risk factors. If your HDL cholesterol is low, they may recommend lifestyle changes or medications to help raise it.
How to Raise HDL Cholesterol
Dietary Changes
Incorporate Healthy Fats
Eating healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, avocados, and fatty fish, can help raise HDL cholesterol levels. These fats are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to increase HDL cholesterol and improve heart health.
Increase Soluble Fiber Intake
Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, beans, and fruits, can help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol. It works by binding to cholesterol in the digestive system and removing it from the body.
Limit Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates
Reducing your intake of sugar and refined carbohydrates can help raise HDL cholesterol levels. These foods can increase triglycerides, which are associated with lower HDL cholesterol.
Exercise Regularly
Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercise, such as walking, jogging, or cycling, has been shown to raise HDL cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to see the benefits.
Strength Training
In addition to aerobic exercise, strength training can also help improve HDL cholesterol levels. Building muscle mass through resistance exercises can increase your metabolic rate and contribute to better cholesterol levels.
Quit Smoking
If you smoke, quitting can significantly raise your HDL cholesterol levels. The benefits of quitting smoking are almost immediate, with HDL cholesterol levels starting to improve within weeks of stopping.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Losing excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, can help raise HDL cholesterol levels. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of your body weight can make a significant difference.
Medications
Statins
Statins are commonly prescribed to lower LDL cholesterol, but they can also have a modest effect on raising HDL cholesterol levels. Your healthcare provider may recommend statins if your cholesterol levels are not well-controlled through lifestyle changes alone.
Niacin
Niacin, a B vitamin, has been shown to raise HDL cholesterol levels. However, it is not commonly used as a first-line treatment due to potential side effects. Your healthcare provider may consider niacin if other treatments are not effective.
Fibrates
Fibrates are another class of medications that can help raise HDL cholesterol levels. They are often used in combination with other cholesterol-lowering medications.
Limit Alcohol Intake
Moderate alcohol consumption, particularly red wine, has been associated with higher HDL cholesterol levels. However, excessive alcohol consumption can have the opposite effect and should be avoided.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Management
Healthy Eating Habits
Adopting a heart-healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help maintain optimal HDL cholesterol levels. Avoiding processed foods and excessive sugar is also crucial.
Consistent Exercise Routine
Maintaining a regular exercise routine is essential for long-term management of HDL cholesterol levels. Consistency is key, and even small increases in physical activity can have a positive impact.
Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups and monitoring of your cholesterol levels are important for early detection and management of low HDL cholesterol. Your healthcare provider can help you stay on track with your goals and make adjustments as needed.
The Importance of HDL Cholesterol in Overall Health
Beyond Heart Health
While HDL cholesterol is primarily known for its role in heart health, it also has other important functions in the body. HDL cholesterol has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can protect against various diseases.
Mental Health Connection
Emerging research suggests a link between HDL cholesterol levels and mental health. Low HDL cholesterol may be associated with an increased risk of depression and cognitive decline. Maintaining healthy HDL cholesterol levels could support brain health and overall well-being.
Longevity and Quality of Life
Maintaining healthy HDL cholesterol levels is not just about preventing disease; it’s also about enhancing your quality of life and longevity. By taking steps to raise your HDL cholesterol, you can improve your overall health and enjoy a longer, healthier life.
Conclusion
Low HDL cholesterol is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, stroke, and other health issues. Understanding the causes, risks, and strategies for managing low HDL cholesterol is crucial for maintaining your heart health and overall well-being. By making lifestyle changes such as improving your diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking, you can raise your HDL cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of serious health problems. Regular health check-ups and open communication with your healthcare provider will ensure that you stay on track with your goals and live a healthier, more fulfilling life.