Electrocardiograms (ECGs or EKGs) are essential tools used in the medical field to monitor heart health and diagnose various cardiac conditions. Understanding the correct placement of ECG leads is crucial for obtaining accurate readings. In this article, we will discuss “ECG where to put leads,” explaining the different lead placements, their importance, and how they help in diagnosing heart issues.
1. Introduction to ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart over a period. The heart generates electrical impulses that stimulate heartbeats, and these impulses can be detected through electrodes placed on the skin. An ECG provides vital information about the heart’s rhythm, size, and position, as well as potential issues such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac diseases.
Understanding “ECG where to put leads” is essential for healthcare providers who administer the test. Proper lead placement ensures accurate readings, which can be critical for timely diagnosis and treatment.
2. Importance of Lead Placement
The accurate placement of leads is crucial for several reasons:
- Diagnostic Accuracy: Incorrect lead placement can lead to misinterpretation of the heart’s electrical activity, resulting in false diagnoses.
- Patient Safety: Accurate ECG readings can help prevent potentially life-threatening conditions from going undetected.
- Monitoring Heart Health: Continuous ECG monitoring in clinical settings requires correct lead placement for reliable data.
- Standardization: Proper lead placement follows standardized protocols, which allows for consistent results across different healthcare providers.
3. Types of ECG Leads
ECG leads can be categorized into two main types: limb leads and chest leads. Understanding these categories helps in grasping the basics of lead placement.
3.1. Limb Leads
Limb leads are the first set of electrodes used in an ECG. They are placed on the arms and legs, creating a triangle around the heart. The three standard limb leads are:
- Lead I: Measures the voltage difference between the left arm (LA) and the right arm (RA).
- Lead II: Measures the voltage difference between the left leg (LL) and the right arm (RA).
- Lead III: Measures the voltage difference between the left leg (LL) and the left arm (LA).
In addition to these three leads, there are also augmented leads, which include:
- aVR (augmented Vector Right): Measures voltage between the right arm and the average of the left arm and left leg.
- aVL (augmented Vector Left): Measures voltage between the left arm and the average of the right arm and left leg.
- aVF (augmented Vector Foot): Measures voltage between the left leg and the average of the right arm and left arm.
3.2. Chest Leads
Chest leads, also known as precordial leads, provide a view of the heart’s electrical activity from the front. They are labeled V1 through V6 and are placed across the chest in specific positions to provide a comprehensive view of the heart.
- V1: Fourth intercostal space, right sternal border
- V2: Fourth intercostal space, left sternal border
- V3: Midway between V2 and V4
- V4: Fifth intercostal space, left midclavicular line
- V5: Anterior axillary line at the same level as V4
- V6: Midaxillary line at the same level as V4 and V5
4. Standard Lead Placement Protocol
The standard lead placement protocol is critical to ensure that all healthcare providers can achieve consistency in ECG recordings. The protocol outlines the specific positions for each lead and helps minimize variations that could affect results.
- Limb leads should be placed at specific points on the limbs. The right arm lead (RA) goes on the right wrist or upper arm, the left arm lead (LA) on the left wrist or upper arm, the right leg lead (RL) on the right ankle or lower leg, and the left leg lead (LL) on the left ankle or lower leg.
- Chest leads require careful positioning on the chest wall. This ensures the best view of the heart’s electrical activity.
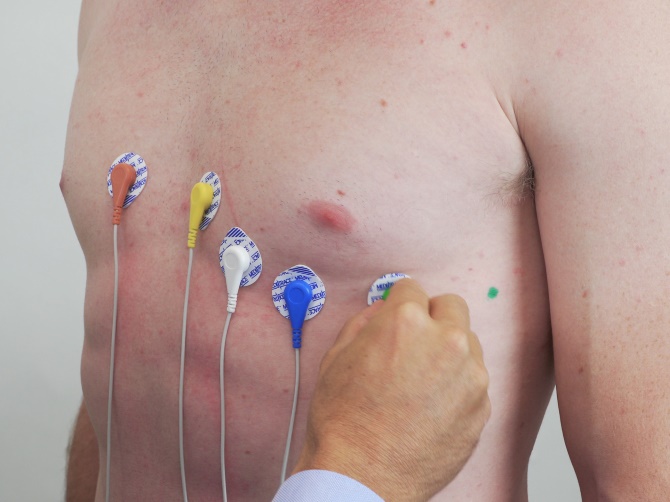
5. Step-by-Step Guide for Lead Placement
To properly conduct an ECG, follow this step-by-step guide for lead placement:
5.1. Limb Lead Placement
- Prepare the Skin: Ensure the skin is clean and dry. Shave or clean any excess hair to improve electrode contact.
- Position the Patient: Have the patient lie down comfortably, with their arms and legs exposed.
- Place the Electrodes:
- Right Arm (RA): Place the electrode on the right wrist or upper arm.
- Left Arm (LA): Place the electrode on the left wrist or upper arm.
- Right Leg (RL): Place the electrode on the right ankle or lower leg.
- Left Leg (LL): Place the electrode on the left ankle or lower leg.
5.2. Chest Lead Placement
- Locate Anatomical Landmarks:
- Find the sternal notch (the U-shaped dip at the base of the neck).
- Count down to the fourth intercostal space (the space between the ribs).
- Place the Electrodes:
- V1: Place at the fourth intercostal space, right sternal border.
- V2: Place at the fourth intercostal space, left sternal border.
- V3: Place midway between V2 and V4.
- V4: Place at the fifth intercostal space, left midclavicular line.
- V5: Place at the anterior axillary line at the same level as V4.
- V6: Place at the midaxillary line at the same level as V4 and V5.
- Connect the Wires: Attach the ECG leads to their corresponding electrodes, ensuring secure connections.
6. Common Mistakes in Lead Placement
Even experienced practitioners can make mistakes when placing ECG leads. Some common errors include:
- Incorrect Lead Placement: Placing electrodes too high or low can lead to misleading results.
- Electrode Reversal: Accidentally swapping the electrodes for different limbs can distort the reading.
- Improper Skin Preparation: Failing to clean or shave the skin can lead to poor electrode contact and unreliable readings.
- Neglecting Patient Positioning: Not positioning the patient correctly can affect the quality of the ECG.
7. Importance of Proper Lead Placement
Proper lead placement is vital for several reasons:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Correct readings allow healthcare providers to accurately diagnose and treat heart conditions.
- Effective Monitoring: Continuous monitoring requires precise lead placement to ensure the heart’s activity is tracked accurately.
- Preventing Errors: Understanding the common mistakes and how to avoid them helps maintain high standards of patient care.
- Consistency in Results: Standardization in lead placement allows for comparability of ECGs across different settings and times.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding “ECG where to put leads” is fundamental for anyone involved in cardiac care. Proper lead placement is crucial for accurate ECG readings, which in turn are essential for diagnosing and monitoring heart conditions. By following standardized protocols for both limb and chest lead placements, healthcare providers can ensure they obtain reliable results that contribute to effective patient care.
9. References
- Zimetbaum, P., & Dwyer, E. M. (2019). The Clinical Electrocardiogram: A Practical Guide. John Wiley & Sons.
- Chung, M. K., et al. (2020). Electrocardiography: Principles and Practice. Springer.
- Kowey, P. R., et al. (2018). Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology: A Global Perspective. Springer.
- Garson, A., & Dick, M. (2018). Clinical Practice of Electrocardiography. Wiley-Blackwell.
This comprehensive guide should serve as a valuable resource for anyone seeking to understand the intricacies of ECG lead placement, ensuring that accurate heart health assessments are made consistently and effectively.