Pneumonia is a serious respiratory infection that can lead to various symptoms, one of which may include coughing up white foamy mucus. This symptom can be alarming and is often a sign that the infection is affecting the lungs’ ability to function properly. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what coughing up white foamy mucus pneumonia means, the potential causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs typically caused by infections. These infections can be viral, bacterial, or fungal. When the lungs become inflamed, they fill with fluid or pus, making breathing difficult and leading to a range of symptoms. Coughing up white foamy mucus is one such symptom that can indicate pneumonia.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Understanding the symptoms of pneumonia is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Cough: Often persistent and may produce mucus.
- Fever: A high temperature can be a sign of infection.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling out of breath.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest area.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak.
Coughing up white foamy mucus is particularly concerning because it may indicate that the mucus is being mixed with the fluid in the lungs.
What Does White Foamy Mucus Mean?
White foamy mucus is a type of expectoration that can occur with various respiratory conditions, including pneumonia. This mucus is typically less thick and more frothy compared to the yellow or green mucus that can be produced with bacterial infections.
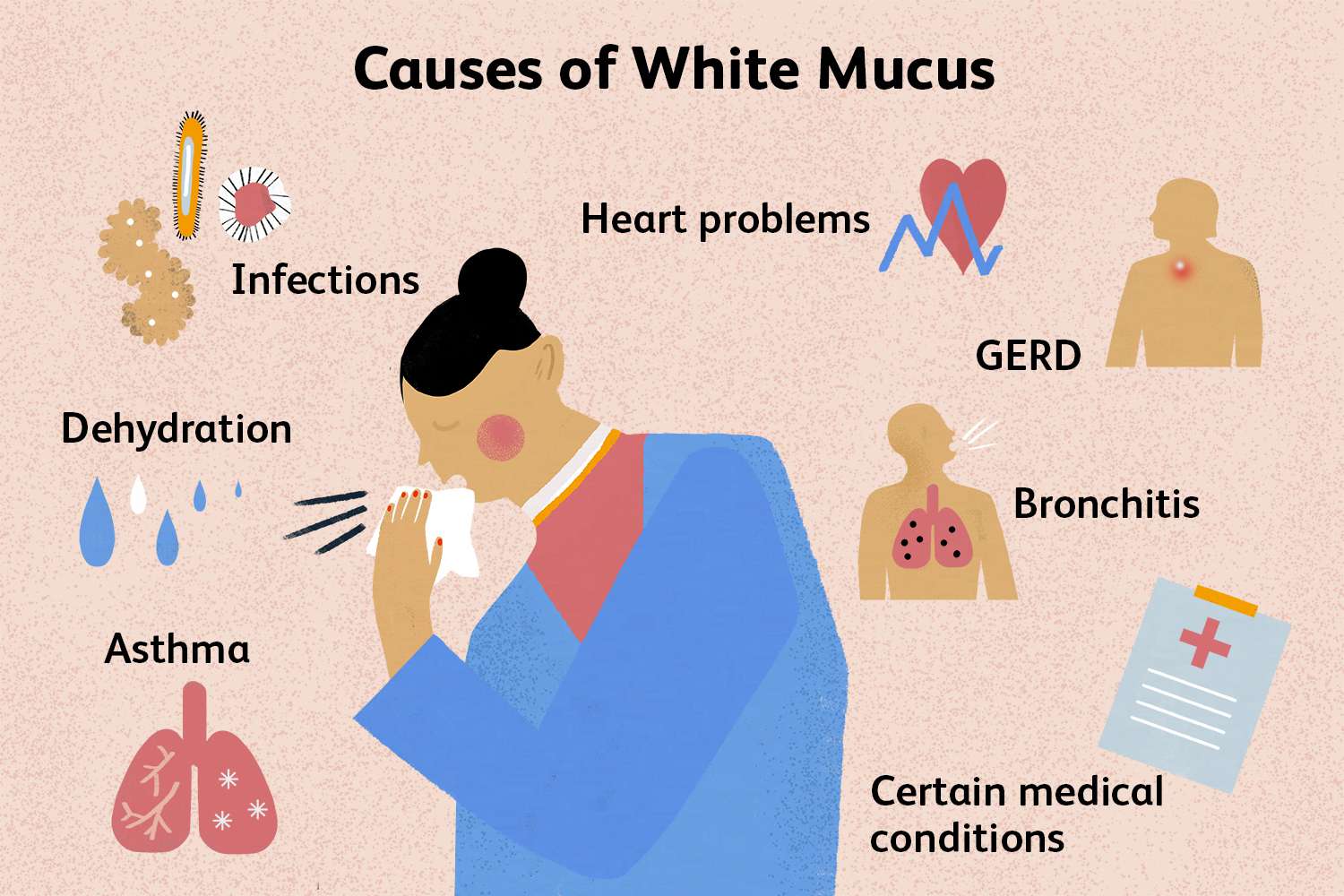
Causes of White Foamy Mucus
White foamy mucus in pneumonia can result from several underlying conditions:
- Viral Pneumonia: Often caused by influenza or other viruses, this type of pneumonia can lead to a white, frothy mucus as the body attempts to clear the infection.
- Atypical Pneumonia: Caused by less common bacteria like Mycoplasma pneumoniae, it can result in milder symptoms, including white foamy mucus.
- Pulmonary Edema: Sometimes associated with pneumonia, this condition involves fluid buildup in the lungs, which can produce foamy mucus.
- Chronic Conditions: Long-term respiratory issues such as chronic bronchitis or asthma can also cause the production of white foamy mucus.
Diagnosis of Pneumonia
Diagnosing pneumonia involves several steps to determine the exact cause and severity of the condition. The process generally includes:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will review symptoms and listen to the lungs with a stethoscope.
- Chest X-Ray: This imaging test helps visualize the lungs and identify areas of inflammation or fluid buildup.
- Sputum Test: Analyzing mucus can help identify the specific pathogen causing the infection.
- Blood Tests: These can reveal markers of infection and inflammation.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia
Treating pneumonia involves addressing the infection and managing symptoms. Treatment options vary based on the type and severity of pneumonia:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics are commonly prescribed.
- Antiviral Medications: If the pneumonia is viral, antiviral drugs may be used.
- Antifungal Medications: In cases of fungal pneumonia, antifungal treatments are necessary.
- Supportive Care: This includes rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and pain.
- Hospitalization: Severe cases may require hospitalization for more intensive treatment and monitoring.
Home Care and Management
For less severe cases, managing pneumonia at home can be effective. Key strategies include:
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus and ease coughing.
- Resting: Adequate rest supports the immune system’s ability to fight the infection.
- Humidifiers: Adding moisture to the air can ease coughing and breathing difficulties.
- Avoiding Irritants: Stay away from smoke and other irritants that can worsen symptoms.
Complications of Pneumonia
Without proper treatment, pneumonia can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Respiratory Failure: Severe pneumonia can impair lung function to the point where oxygen levels drop dangerously.
- Sepsis: A severe, widespread infection that can spread to other parts of the body.
- Lung Abscesses: Pockets of pus that can form in the lungs.
Prevention of Pneumonia
Preventive measures can help reduce the risk of pneumonia, including:
- Vaccinations: Getting vaccinated against influenza and pneumococcal pneumonia.
- Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet, staying active, and avoiding smoking.
Conclusion
Coughing up white foamy mucus pneumonia is a symptom that requires attention and proper diagnosis. Understanding its potential causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking timely treatment are crucial for managing this condition effectively. By following medical advice and taking preventive measures, individuals can recover from pneumonia and reduce the risk of complications.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of pneumonia with a focus on coughing up white foamy mucus. If you experience this symptom, consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.