Tuberculosis, often called TB, is a sickness that affects many people around the world. It is a disease caused by tiny germs that can hide in our lungs and make us sick. While TB has been around for a long time, many people still don’t know a lot about it. In this article, we will explore what tuberculosis is, how it spreads, how to recognize it, and ways to prevent and treat it. So, let’s dive in and learn together!
What is Tuberculosis?
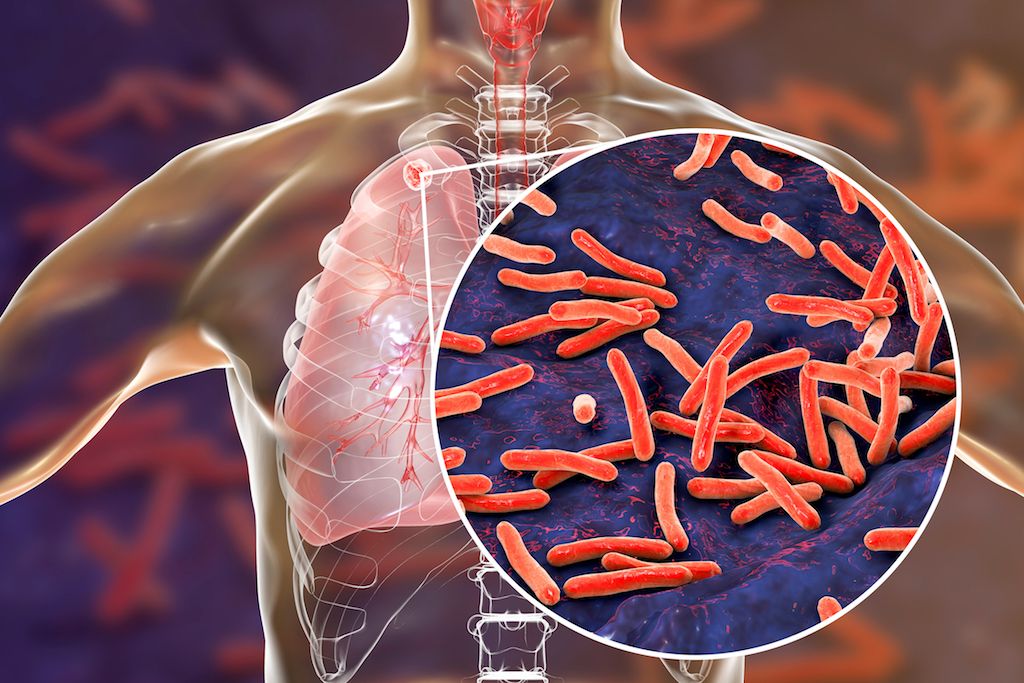
Tuberculosis is a contagious disease caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This germ usually lives in the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body, like the kidneys, spine, and brain. When a person with TB coughs or sneezes, tiny droplets containing the bacteria can spread into the air. If someone else breathes in these droplets, they can catch the disease. It’s important to note that not everyone who breathes in these germs will get sick. Our bodies are sometimes able to fight off the bacteria without getting ill.
How Does TB Spread?
You might be wondering how tuberculosis spreads so easily. It is primarily spread through the air. Imagine someone with TB is in a room with you, and they cough. They release tiny particles into the air, which can hang around for a while. If you breathe in those particles, there’s a chance you could get infected. It’s similar to catching a cold or the flu. However, just like with those illnesses, not everyone who breathes in the germs will become sick. Some people can carry the germs without ever getting sick themselves, which is called latent TB infection.
Who is at Risk?
Certain groups of people are at a higher risk of developing tuberculosis. For example, individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or people undergoing chemotherapy, are more likely to get sick. Additionally, people living in crowded places, like prisons or shelters, can spread TB more easily. It’s also important to mention that TB is more common in some parts of the world, especially in countries with high levels of poverty and limited access to healthcare.
Signs and Symptoms of Tuberculosis
If someone is infected with tuberculosis, they may experience various symptoms. The most common signs include a persistent cough that lasts for more than three weeks, chest pain, and coughing up blood. People with TB may also feel tired all the time, lose weight without trying, have a fever, and sweat at night. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is crucial to see a doctor as soon as possible. Early detection can make a big difference in treatment and recovery.
Diagnosing Tuberculosis
Doctors use different tests to diagnose tuberculosis. One of the most common tests is called the tuberculin skin test. In this test, a small amount of a substance called tuberculin is injected just under the skin of your arm. After 48 to 72 hours, the doctor will check for a reaction, which usually looks like a raised bump. If the bump is big enough, it might mean that you have been exposed to the TB germ. However, other tests, like chest X-rays or sputum tests, might be needed to confirm a diagnosis.
Treatment for Tuberculosis
If someone is diagnosed with tuberculosis, there is good news: it is treatable! Doctors usually prescribe a combination of antibiotics to help fight the bacteria. It’s essential to take all the medications as directed, even if you start to feel better after a few days. This is because stopping treatment early can lead to drug-resistant TB, which is much harder to treat. Treatment usually lasts for about six months, but it can vary based on the person’s health and the type of TB they have.
The Importance of Completing Treatment
Completing the full course of TB treatment is crucial. Imagine you are building a strong wall to protect your house. If you only build part of the wall, it won’t be strong enough to keep out bad weather or unwanted visitors. Similarly, taking all of your medications ensures that the TB bacteria are completely gone from your body. If you don’t finish your treatment, the bacteria can come back, and they may become resistant to the drugs. This means that the medicine won’t work anymore, making it much harder to get better.
Preventing Tuberculosis
Preventing tuberculosis is possible, and it starts with understanding how the disease spreads. Here are some easy steps to help prevent TB:
- Get Tested: If you think you might have been exposed to someone with TB or if you are in a high-risk group, getting tested can help catch the disease early.
- Stay Away from Sick People: If someone is coughing a lot or showing other signs of TB, it’s best to keep your distance until they have seen a doctor.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Cover your mouth when you cough or sneeze and wash your hands regularly to keep germs from spreading.
- Get Vaccinated: In some countries, there is a vaccine called BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin) that can help prevent TB, especially in young children.
- Eat Healthy: Eating a balanced diet helps strengthen your immune system, making it easier for your body to fight off infections like TB.
- Avoid Crowded Places: If possible, try to stay away from crowded areas, especially if someone nearby is coughing or appears sick.
By following these simple steps, you can help protect yourself and those around you from tuberculosis.
The Global Impact of Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is not just a personal health issue; it is a global health challenge. Each year, millions of people around the world are affected by TB, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. The World Health Organization (WHO) works hard to track and control TB cases worldwide. They set goals to reduce TB rates and promote awareness about prevention and treatment. Despite the challenges, there is hope. Increased funding for research, better access to healthcare, and community education are helping to reduce the impact of TB globally.
Living with Tuberculosis
If someone has been diagnosed with tuberculosis, it can be a challenging experience. They may feel scared or alone, but it’s essential to remember that they are not alone. Support from family and friends can make a significant difference. Joining a support group can also help individuals share their feelings and learn from others who are going through similar experiences.
It’s important for individuals with TB to take care of their mental and emotional health while undergoing treatment. Practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, and maintaining a positive attitude can aid in their recovery journey.
The Future of Tuberculosis Treatment
Researchers and healthcare professionals are continually looking for new ways to improve tuberculosis treatment and prevention. There are exciting developments in the field, such as new vaccines, shorter treatment courses, and better diagnostic tests. These advancements could significantly reduce the number of TB cases worldwide and make it easier for people to access effective treatments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tuberculosis is a significant health issue that requires our attention and action. By understanding how TB spreads, recognizing its symptoms, and knowing how to prevent and treat it, we can protect ourselves and others. Remember, tuberculosis is treatable, and many people recover completely with the right care. Let’s continue to raise awareness and support efforts to combat this disease. Together, we can make a difference in the fight against tuberculosis.