The human body is a complex system composed of bones, muscles, and tissues that work together to support movement, stability, and protection. One such crucial bone is the sacrum, located at the base of the spine. Despite being a lesser-known term for many, the sacrum plays a vital role in the body’s overall structure and movement. In this article, we will dive deep into what the sacrum is, its anatomy, its role in daily functioning, and its importance for health and well-being.
What is the Sacrum?
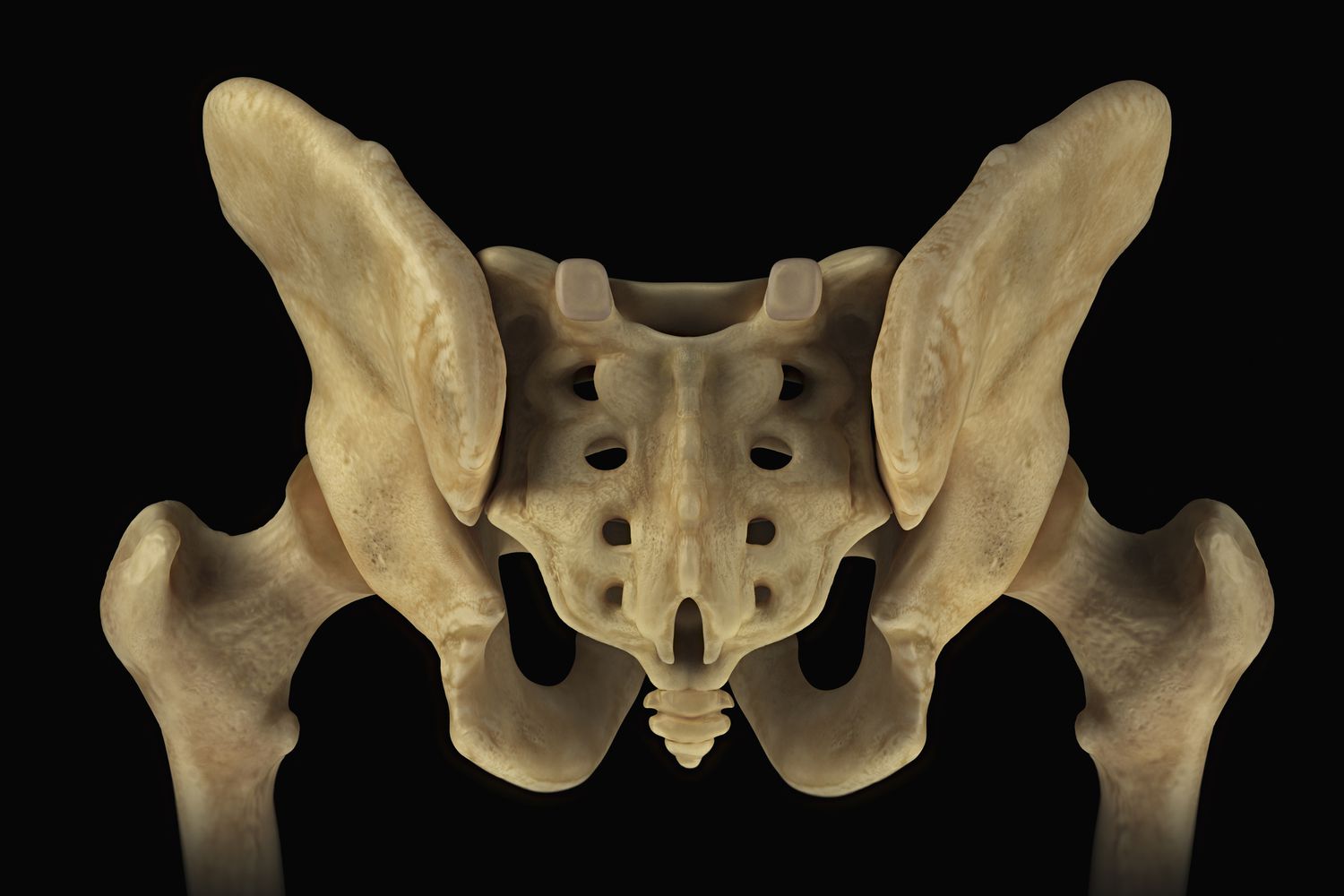
The sacrum is a large, triangular-shaped bone situated at the base of the spine and above the coccyx (tailbone). It forms the posterior part of the pelvis and is essential in connecting the spine to the hip bones. Its role in distributing weight and maintaining balance is crucial for standing, walking, and various other physical activities.
Anatomical Location of the Sacrum
To better understand the significance of the sacrum, let’s explore its location within the body. The sacrum is positioned between the lumbar spine (lower back) and the coccyx. It forms the back wall of the pelvis, connecting with the ilium bones on either side through the sacroiliac joints. This connection helps provide stability to the pelvis while allowing the transfer of weight from the upper body to the legs.
The Formation and Structure of the Sacrum
The sacrum develops from five individual vertebrae, known as S1 to S5. These vertebrae fuse together during adulthood, typically around the age of 30, to form a single solid bone. This fusion process creates a strong, stable structure that supports the upper body and aids in movement.
The sacrum features four pairs of openings known as sacral foramina. These openings allow nerves and blood vessels to pass through, connecting the spinal cord to the lower body. The anterior (front) surface of the sacrum is concave, while the posterior (back) surface is convex, giving the sacrum its characteristic curved shape. This shape is integral to its function in supporting weight and facilitating movement.
The Role of the Sacrum in the Human Body
The sacrum serves several essential functions, making it one of the most important bones in the human skeleton. Its primary roles include providing structural support, protecting the spinal cord, facilitating movement, and aiding in weight distribution.
1. Structural Support
One of the most significant functions of the sacrum is providing structural support for the upper body. As the central point of connection between the spine and the pelvis, the sacrum helps maintain stability and balance. Without the sacrum, the spine would not have a stable base, making it difficult for the body to stand upright or engage in complex movements like walking or running.
2. Weight Distribution and Balance
The sacrum is crucial for evenly distributing the weight of the upper body to the lower body, specifically the legs. As part of the pelvic girdle, it acts as a bridge between the spine and the legs, transferring the load during standing, walking, and other physical activities. This distribution of weight is necessary for maintaining balance and preventing excess strain on the lower back and legs.
3. Protection of Nerves and Blood Vessels
As mentioned earlier, the sacrum contains sacral foramina, which are openings that allow for the passage of nerves and blood vessels. These nerves, known as sacral nerves, are responsible for sending signals to and from the lower extremities, controlling sensations and movements in the legs, feet, and pelvic region. The sacrum’s design helps protect these vital nerves from injury.
4. Supporting Pelvic Organs
The sacrum also plays a role in supporting the organs of the pelvic region. These include the bladder, intestines, and reproductive organs. By helping form the back wall of the pelvis, the sacrum provides a stable structure that keeps these organs in place and ensures they function properly.
Sacroiliac Joints: The Connection between Sacrum and Ilium
One of the most critical connections involving the sacrum is the sacroiliac joint (SI joint). These joints are located on either side of the sacrum, where it connects with the ilium (the large, wing-like bones of the pelvis). The SI joints are essential for transferring weight between the spine and the lower body, playing a key role in movement and stability.
Structure and Function of the Sacroiliac Joints
The sacroiliac joints are unique in that they allow for limited movement. While most joints in the body enable a wide range of motion, the SI joints are designed to be more stable, providing minimal movement to ensure that the pelvis remains secure while supporting the weight of the upper body.
The primary function of the sacroiliac joints is to absorb and distribute shock from the upper body to the legs during activities like walking, running, and jumping. The limited movement in these joints also helps reduce the risk of injury by preventing excessive strain on the spine and pelvis.
Common Sacroiliac Joint Problems
While the sacroiliac joints are built for stability, they are not immune to problems. Some individuals experience pain or discomfort in this area due to a condition known as sacroiliac joint dysfunction. This condition can be caused by injury, pregnancy, arthritis, or even uneven leg lengths. When the sacroiliac joints are not functioning properly, it can lead to lower back pain, hip pain, and even discomfort in the legs.
Treatment for sacroiliac joint dysfunction often involves physical therapy, exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the pelvis, and in some cases, injections or surgery. Proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing this condition and preventing long-term damage.
The Importance of the Sacrum in Movement
As a central component of the pelvis, the sacrum is essential for movement. Its role in weight distribution, stability, and balance directly affects how we walk, run, and perform everyday tasks. Let’s explore how the sacrum contributes to various types of movement.
Walking and Running
During walking and running, the sacrum helps distribute the weight of the upper body to the lower limbs, enabling smooth, efficient movement. The connection between the sacrum and the pelvis provides the necessary support and balance needed to propel the body forward without straining the spine or legs. Additionally, the sacrum’s ability to absorb shock ensures that the spine and pelvis are protected from the impact of each step.
Bending and Lifting
The sacrum is also vital for activities that involve bending and lifting. When you bend over to pick something up, the sacrum helps stabilize the spine and pelvis, preventing injury to the lower back. Similarly, during lifting, the sacrum plays a role in ensuring that the weight is evenly distributed and that the spine remains properly aligned.
Twisting and Rotating Movements
Although the sacroiliac joints limit excessive movement, they still allow for some degree of flexibility, particularly when it comes to twisting and rotating movements. The sacrum’s connection to the pelvis enables the body to rotate and twist while maintaining balance and stability. This is essential for activities like turning, dancing, or even reaching for objects.
The Sacrum and the Nervous System
In addition to its structural functions, the sacrum is closely linked to the nervous system. The sacral nerves, which pass through the sacral foramina, are part of the larger network of nerves that make up the peripheral nervous system. These nerves control sensations and movements in the lower half of the body, including the legs, feet, and pelvic region.
The Sacral Plexus
The sacral plexus is a network of nerves that arises from the sacral region of the spine. It plays a critical role in controlling motor and sensory functions in the lower body. The sciatic nerve, the largest nerve in the human body, originates from the sacral plexus and extends down the leg, providing sensation and movement to the lower limbs.
Sacral Nerve Impingement
Sometimes, the sacral nerves can become compressed or irritated, leading to a condition known as sacral nerve impingement or sacral radiculopathy. This condition can cause pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the lower back, buttocks, and legs. Sacral nerve impingement is often caused by conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or injury to the sacrum.
Treatment for sacral nerve impingement typically involves physical therapy, medication, and in some cases, surgery. Addressing the underlying cause of the nerve compression is essential for relieving symptoms and preventing further damage.
The Sacrum in Pregnancy and Childbirth
The sacrum plays a unique role in pregnancy and childbirth, as it helps accommodate the changes in a woman’s body during pregnancy and aids in the delivery process.
Changes in the Sacrum During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the body undergoes various changes to support the growing fetus. One of these changes is the loosening of the ligaments that connect the sacrum to the pelvis. This increased flexibility allows the pelvis to expand as the baby grows, making it easier for the mother to carry the additional weight.
However, the increased mobility of the sacroiliac joints during pregnancy can sometimes lead to discomfort or pain in the lower back or hips. This condition is often referred to as pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain (PGP) and can be managed with physical therapy, exercises, and support belts.
The Role of the Sacrum in Childbirth
During childbirth, the sacrum plays a crucial role in allowing the baby to pass through the birth canal. As the baby moves through the pelvis, the sacrum tilts and shifts to create more space for the baby to be delivered. This process is known as sacral nutation and is an essential part of the birthing process.
Common Sacral Disorders and Injuries
Like any other bone in the body, the sac
rum is susceptible to injuries and disorders. Some of the most common sacral issues include fractures, arthritis, and sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
Sacral Fractures
A sacral fracture is a break in the sacrum, often caused by trauma such as a fall, car accident, or sports injury. Sacral fractures can vary in severity, ranging from minor cracks to more complex breaks that involve other parts of the pelvis or spine. Symptoms of a sacral fracture may include pain in the lower back, buttocks, or hips, difficulty walking, and numbness or tingling in the legs.
Treatment for a sacral fracture depends on the severity of the injury. In some cases, rest and physical therapy are sufficient for healing, while more severe fractures may require surgery.
Sacroiliitis
Sacroiliitis is an inflammation of the sacroiliac joints, which can cause pain in the lower back, buttocks, and legs. This condition is often associated with inflammatory diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis. Sacroiliitis can be treated with medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage inflammation and reduce pain.
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
As mentioned earlier, sacroiliac joint dysfunction occurs when the SI joints are not functioning properly, leading to pain and discomfort in the lower back, hips, and legs. This condition can be caused by injury, arthritis, or pregnancy and is often treated with physical therapy, exercises, and sometimes injections or surgery.
Conclusion
The sacrum may not be the most well-known bone in the human body, but it plays a vital role in supporting movement, stability, and overall health. From its connection to the pelvis and the spine to its involvement in nerve function and weight distribution, the sacrum is an essential part of the body’s structure. Understanding the sacrum’s anatomy and function can help individuals recognize the importance of maintaining sacral health, especially in cases of injury, pain, or dysfunction.
By taking care of the sacrum through proper posture, exercise, and medical attention when needed, we can ensure that this vital bone continues to support our bodies in movement and balance for years to come.