Acetic acid is a colorless liquid organic compound with a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell. It is widely known as the main component of vinegar, which contains about 4-8% acetic acid by volume. This article will delve deep into the nature of acetic acid, exploring its chemical structure, physical properties, methods of production, various applications, and its significance in both industrial and everyday contexts.
What is Acetic Acid?
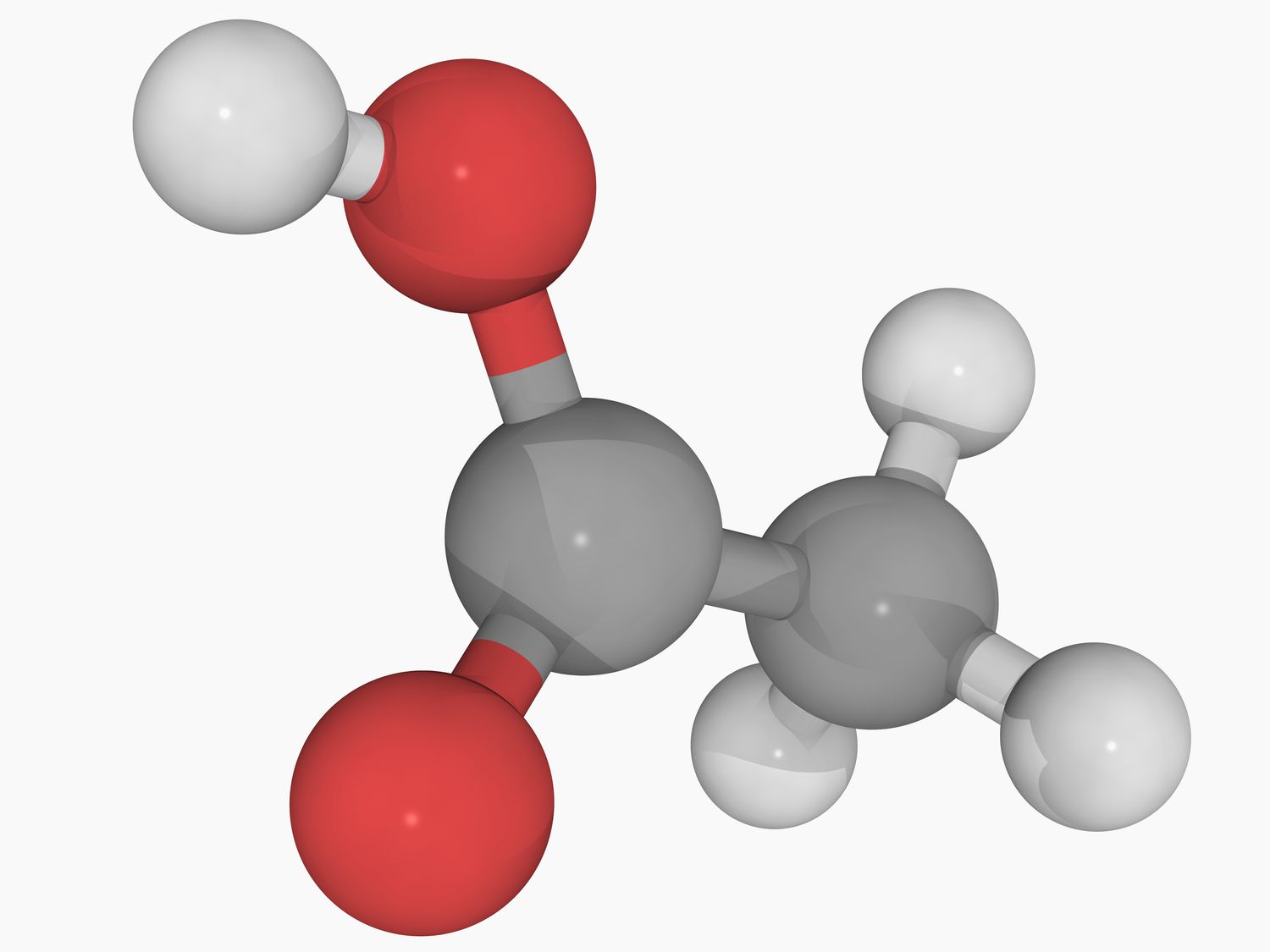
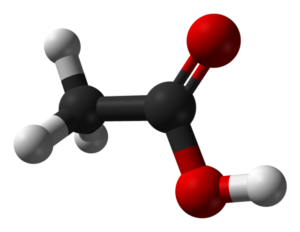
Acetic acid, also known as ethanoic acid, is a simple carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH₃COOH. It consists of two carbon atoms, four hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. This compound is highly versatile and is used in various fields, including food production, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing.
Chemical Structure of Acetic Acid
Acetic acid has a simple molecular structure. It is made up of two main parts:
- Methyl Group (CH₃): This is the hydrocarbon portion of the molecule.
- Carboxyl Group (COOH): This part contains the acidic component, responsible for its properties as an acid.
The structure can be visualized as follows:
O
||
CH₃—C—OHPhysical Properties of Acetic Acid
Acetic acid has several physical properties that define its characteristics:
- Appearance: It is a colorless liquid.
- Odor: It has a strong, pungent smell, often associated with vinegar.
- Taste: It has a sour taste.
- Boiling Point: Acetic acid has a boiling point of 118.1°C (244.6°F).
- Solubility: It is miscible with water, meaning it can mix uniformly with water in any proportion.
- Density: The density of acetic acid is 1.049 g/cm³ at 20°C (68°F).
Acidity of Acetic Acid
Acetic acid is classified as a weak acid, meaning it does not completely dissociate in water. In an aqueous solution, it partially ionizes to produce acetate ions (CH₃COO⁻) and hydrogen ions (H⁺), contributing to its acidic nature. The dissociation can be represented as follows:
[ \text{CH₃COOH} \rightleftharpoons \text{CH₃COO⁻} + \text{H⁺} ]
The strength of an acid is measured using the pKa value. For acetic acid, the pKa is around 4.76, indicating that it is weaker than strong acids like hydrochloric acid (HCl) but stronger than other weak acids.
Production of Acetic Acid
Acetic acid can be produced through various methods, primarily:
1. Fermentation
One of the oldest methods of producing acetic acid is through the fermentation of carbohydrates. This process involves the conversion of sugars into ethanol by yeast, followed by the oxidation of ethanol into acetic acid by acetic acid bacteria. This method is commonly used in the production of vinegar.
2. Chemical Synthesis
Most acetic acid is produced synthetically through chemical processes. Two primary methods are used:
- Methanol Carbonylation: In this process, methanol reacts with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst (usually rhodium or iridium) to produce acetic acid. This method is widely used in industrial production and is efficient and cost-effective. [ \text{CH₃OH} + \text{CO} \rightarrow \text{CH₃COOH} ]
- Ethylene Oxidation: Ethylene is oxidized to produce acetic acid using a catalyst. This method is less common but still used in some regions.
3. Natural Sources
Acetic acid is also found in various natural sources. For example, it is present in fermented foods, such as pickles and sauerkraut, and is produced by certain bacteria and fungi.
Uses of Acetic Acid
Acetic acid is utilized in a variety of applications across multiple industries. Here are some of the most significant uses:
1. Food Industry
- Vinegar Production: The most well-known use of acetic acid is in the production of vinegar, which is used as a condiment and preservative.
- Flavoring Agent: Acetic acid is used to enhance the flavor of various food products, including salad dressings, sauces, and marinades.
- Preservative: Due to its antibacterial properties, acetic acid helps preserve food by inhibiting the growth of spoilage organisms.
2. Chemical Manufacturing
- Production of Chemicals: Acetic acid is a key raw material in the production of various chemicals, such as acetic anhydride, acetate esters, and various solvents.
- Synthesis of Plastics: It is used in the production of synthetic fibers, plastics, and coatings.
3. Pharmaceutical Industry
- Drug Production: Acetic acid is used in the manufacture of certain pharmaceuticals, including analgesics and antibiotics.
- pH Adjuster: In pharmaceutical formulations, acetic acid can help maintain the desired pH level.
4. Household Uses
- Cleaning Agent: Acetic acid is a common ingredient in household cleaners due to its ability to cut through grease and remove stains.
- Deodorizer: Its strong smell can neutralize odors in various environments.
5. Agriculture
- Herbicide: Acetic acid is sometimes used as a natural herbicide to control weeds in organic farming.
- Soil Conditioner: It can improve soil quality by increasing acidity, which benefits certain plants.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
While acetic acid is safe to use in many applications, it can pose risks if not handled properly. Here are some important safety and environmental considerations:
1. Health Hazards
- Skin and Eye Irritation: Concentrated acetic acid can cause irritation to the skin and eyes. Proper protective equipment should be worn when handling it.
- Inhalation Risks: Inhaling vapors can irritate the respiratory tract, so adequate ventilation is essential when using acetic acid.
2. Environmental Impact
- Biodegradability: Acetic acid is biodegradable and can break down naturally in the environment. However, high concentrations can be harmful to aquatic life.
- Regulations: Various regulations govern the use and disposal of acetic acid to minimize its environmental impact.
Acetic Acid in Everyday Life
Acetic acid is present in many aspects of daily life, often without people realizing it. Here are some common examples:
1. Cooking and Food Preparation
- Vinegar: The most familiar form of acetic acid, vinegar, is used in countless recipes, from salad dressings to pickling vegetables.
- Food Preservation: Home canners often use acetic acid in the form of vinegar to preserve fruits and vegetables.
2. Cleaning
- Natural Cleaner: Many households use vinegar as a natural cleaning solution to disinfect surfaces and remove odors.
- Laundry: Adding vinegar to laundry can help remove odors and brighten whites.
3. Personal Care
- Skincare: Some skincare products contain diluted acetic acid for its exfoliating properties.
- Hair Care: Vinegar rinses are sometimes used to enhance shine and remove residue from hair.
4. Gardening
- Fertilizers: Acetic acid can be found in some organic fertilizers, helping to lower soil pH for acid-loving plants.
Conclusion
Acetic acid is a vital compound with diverse applications and significance in daily life. From its role as the main ingredient in vinegar to its importance in industrial chemical production, acetic acid plays a crucial role in various sectors. Understanding its properties, uses, and safety considerations can help us appreciate this simple yet essential organic compound.
As we continue to explore new methods of production and applications, acetic acid remains a key player in many industries, proving its value beyond its common association with vinegar. Whether in food, cleaning, pharmaceuticals, or agriculture, the impact of acetic acid is far-reaching and significant.
Further Reading
For those interested in learning more about acetic acid, here are some suggested readings:
- The Science of Vinegar – Explore the chemistry and history of vinegar and its uses.
- Acetic Acid Production: A Comprehensive Guide – A detailed look into the industrial processes of acetic acid production.
- Natural Cleaners: The Benefits of Acetic Acid – Discover the various ways to use acetic acid in household cleaning.
By understanding the many facets of acetic acid, we can make informed choices in our daily lives, whether in the kitchen, at work, or in the garden.