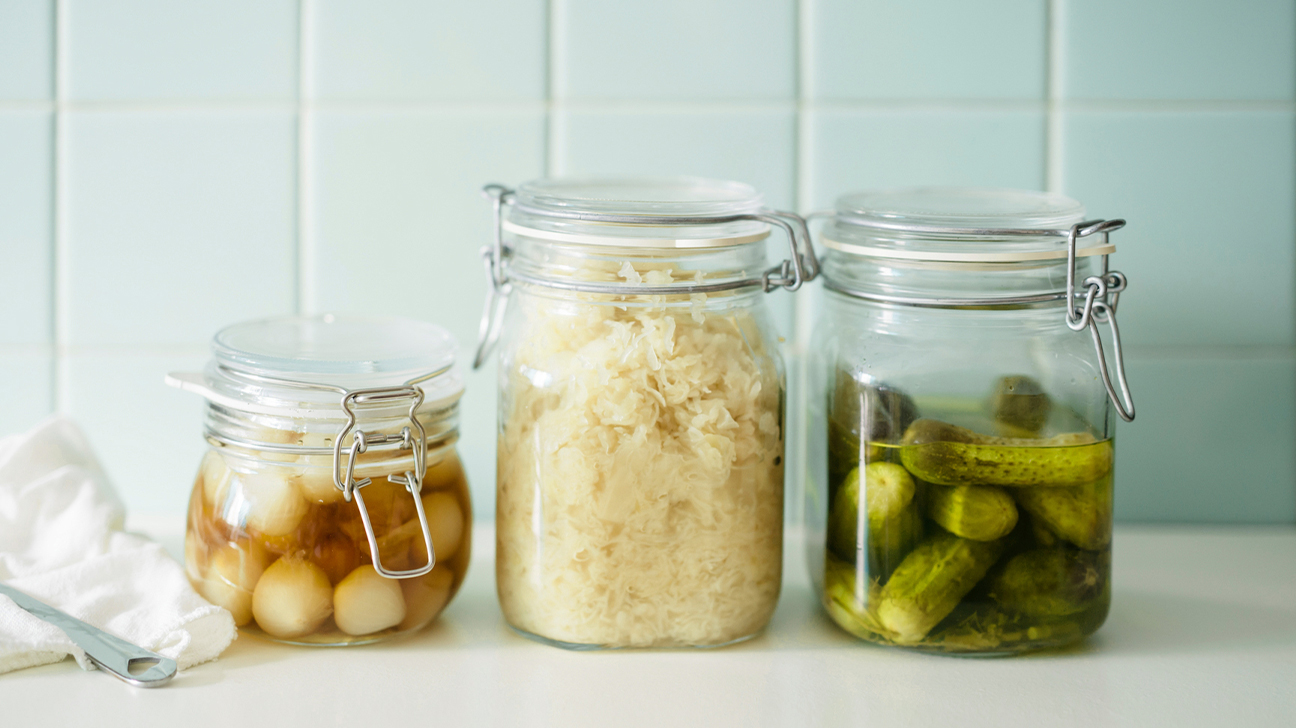
Fermented foods have been a staple in diets around the world for centuries. From yogurt to kimchi, these foods undergo a natural process where microorganisms like bacteria, yeast, and molds convert sugars and starches into acids or alcohol. This article will explore what fermented foods are, their health benefits, various types, and some easy recipes to incorporate them into your diet.
What Are Fermented Foods?
Fermented foods are products made through the controlled microbial growth and the conversion of food components through enzymatic action. During fermentation, the sugars in the food are broken down by bacteria, yeast, or molds, leading to the development of beneficial probiotics. These microorganisms not only enhance the flavors and textures of the food but also contribute to health benefits.
The Process of Fermentation
The fermentation process can be broken down into several stages:
- Preparation: This involves selecting fresh ingredients. Vegetables, fruits, grains, and dairy products can all be fermented.
- Adding Culture: In some cases, specific strains of bacteria or yeast are added to initiate fermentation. In other cases, natural fermentation occurs when wild microorganisms present on the food or in the environment are allowed to proliferate.
- Fermentation: The mixture is kept in a controlled environment, typically at a specific temperature and humidity level. During this time, the microorganisms multiply and begin the process of breaking down the sugars.
- Maturation: The food is allowed to mature, developing its unique flavors and beneficial properties.
- Storage: After fermentation, the product is often stored in a cool place to preserve its freshness and prevent spoilage.
The Health Benefits of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods offer a myriad of health benefits, many of which are linked to their probiotic content. Here are some key advantages:
1. Improved Digestion
Fermented foods contain live bacteria that can aid digestion by breaking down complex carbohydrates and fibers that are hard for the body to digest. This can help alleviate issues like bloating, gas, and constipation.
2. Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
The fermentation process can increase the bioavailability of nutrients, making it easier for the body to absorb vitamins and minerals. For instance, fermented dairy products may allow for better calcium absorption.
3. Strengthened Immune System
Probiotics found in fermented foods can support the immune system by enhancing the gut microbiota, which plays a critical role in immune health. A balanced gut microbiome can reduce the risk of infections and inflammation.
4. Mental Health Benefits
Recent research suggests a connection between gut health and mental well-being. The gut produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, which are essential for mood regulation. Consuming fermented foods may help maintain a healthy gut, potentially improving mood and reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
5. Potential Weight Management
Some studies suggest that probiotics may assist in weight management by influencing metabolism and fat storage. Fermented foods can also help regulate appetite by enhancing satiety.
Popular Types of Fermented Foods
There is a wide variety of fermented foods enjoyed worldwide, each with unique flavors and health benefits. Below are some popular types:
1. Yogurt
Yogurt is one of the most well-known fermented dairy products. Made by fermenting milk with specific bacterial cultures, it is rich in probiotics, calcium, and protein.
2. Sauerkraut
This fermented cabbage dish originates from Germany and is rich in fiber, vitamins C and K, and probiotics. The fermentation process gives sauerkraut its tangy flavor.
3. Kimchi
A staple in Korean cuisine, kimchi is made from fermented vegetables, primarily napa cabbage and radishes, mixed with spices. It is packed with probiotics, vitamins, and minerals.
4. Kefir
Kefir is a fermented milk drink that is similar to yogurt but thinner in consistency. It contains a diverse range of bacteria and yeast, making it a potent source of probiotics.
5. Kombucha
Kombucha is a fermented tea drink made by adding a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) to sweetened tea. It is fizzy and has a slightly tangy taste, and is known for its detoxifying properties.
6. Miso
Miso is a Japanese paste made from fermented soybeans, salt, and a fungus called koji. It is often used in soups, marinades, and dressings, adding umami flavor and health benefits.
7. Tempeh
Tempeh is another fermented soy product originating from Indonesia. It is made from whole soybeans that have been fermented, resulting in a firm texture and nutty flavor. Tempeh is a rich source of protein and can be used as a meat substitute.
8. Pickles
Pickles, often made from cucumbers, are fermented in a brine solution. They can vary in flavor based on the spices used and provide a good source of probiotics.
How to Incorporate Fermented Foods into Your Diet
Adding fermented foods to your diet can be a delicious and nutritious choice. Here are some easy ways to incorporate them:
1. Breakfast
Start your day with a serving of yogurt topped with fruits, nuts, or granola. You can also add kefir to smoothies for a probiotic boost.
2. Snacks
Enjoy sauerkraut or kimchi as a tangy snack. You can also try pickles or miso-based spreads on whole-grain crackers.
3. Lunch
Incorporate fermented foods into your salads. For instance, add kimchi to a mixed greens salad or use miso dressing on steamed vegetables.
4. Dinner
Use tempeh or miso in stir-fries or as a meat substitute in tacos. Fermented sauces, like soy sauce or tamari, can enhance the flavor of your dishes.
5. Beverages
Sip on kombucha for a refreshing drink that also supports gut health. You can find various flavors, or you can brew your own at home.
Simple Recipes for Fermented Foods
1. Homemade Yogurt
Ingredients:
- 4 cups of milk (whole or low-fat)
- 1/4 cup of plain yogurt with live cultures
Instructions:
- Heat the milk in a saucepan over medium heat until it reaches about 180°F (82°C). This helps kill any unwanted bacteria.
- Remove from heat and let it cool to about 110°F (43°C).
- Stir in the plain yogurt until fully mixed.
- Pour the mixture into a clean container and cover it with a lid or cloth.
- Place it in a warm spot (like an oven with the light on) for 6-12 hours.
- Once thickened, refrigerate for a few hours before consuming.
2. Easy Sauerkraut
Ingredients:
- 1 medium head of green cabbage
- 1 tablespoon of sea salt
Instructions:
- Remove the outer leaves of the cabbage and set them aside.
- Finely shred the cabbage and place it in a large bowl.
- Sprinkle salt over the cabbage and massage it until it becomes watery.
- Pack the cabbage tightly into a clean jar, leaving some space at the top.
- Place the reserved cabbage leaves on top to keep the shredded cabbage submerged in its liquid.
- Cover the jar with a cloth and let it ferment at room temperature for about 1-4 weeks, tasting it periodically.
- Once it reaches your desired flavor, seal it with a lid and refrigerate.
3. Kimchi
Ingredients:
- 1 medium napa cabbage
- 1/4 cup sea salt
- 4 cups water
- 4 green onions, chopped
- 1 tablespoon grated ginger
- 2 tablespoons minced garlic
- 2 tablespoons sugar
- 1 tablespoon fish sauce
- 2-3 tablespoons Korean red pepper flakes (gochugaru)
Instructions:
- Dissolve salt in water and soak the cabbage in it for 2 hours.
- Rinse and drain the cabbage, then set it aside.
- In a bowl, combine green onions, ginger, garlic, sugar, fish sauce, and gochugaru to make a paste.
- Mix the paste with the cabbage until fully coated.
- Pack the kimchi tightly into a clean jar and leave some space at the top.
- Cover and let it ferment at room temperature for 1-5 days, then refrigerate.
4. Kombucha
Ingredients:
- 1 cup of sugar
- 8 bags of black tea
- 2 cups of starter tea (from a previous batch or store-bought)
- 1 SCOBY (symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast)
Instructions:
- Boil 4 cups of water and dissolve the sugar in it.
- Add tea bags and steep for about 15 minutes. Remove tea bags and let the mixture cool.
- Pour the cooled tea into a large jar and add 4 cups of water and starter tea.
- Gently place the SCOBY on top of the tea.
- Cover the jar with a cloth and secure it with a rubber band.
- Let it ferment in a warm, dark place for 7-14 days, tasting periodically.
- Once it reaches your desired flavor, remove the SCOBY and store the kombucha in bottles.
Conclusion
Fermented foods are not just delicious; they also offer numerous health benefits that can enhance your well-being. By incorporating these foods into your diet, you can improve digestion, boost your immune system, and enjoy a greater variety of flavors in your meals. Whether you choose to buy fermented foods from the store or make your own at