The keto diet, short for the ketogenic diet, has gained immense popularity over the years as a weight-loss strategy and a potential solution for various health issues. This low-carb, high-fat diet aims to shift the body’s metabolism from burning glucose (sugar) to burning fat for fuel. In this article, we will explore the principles of the keto diet, its benefits, potential risks, meal planning, and tips for success.
What is the Keto Diet?
The keto diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that significantly reduces carbohydrate intake while increasing fat consumption. This dietary approach aims to trigger a metabolic state called ketosis, where the body becomes highly efficient at burning fat for energy. By drastically cutting carbs and replacing them with fats, the body enters a state of ketosis, leading to various health benefits.
The Science Behind the Keto Diet
When carbohydrates are consumed, the body breaks them down into glucose, which is then used as the primary source of energy. In a keto diet, carbohydrate intake is typically limited to around 20 to 50 grams per day, prompting the body to look for alternative energy sources. In ketosis, the liver converts fats into ketones, which serve as an alternative fuel source for the brain and body.
Key Components of the Keto Diet
To successfully follow the keto diet, it is essential to understand its core components:
1. Macronutrient Ratios
A typical keto diet consists of the following macronutrient ratios:
- Fat: 70-75% of total daily calories
- Protein: 20-25% of total daily calories
- Carbohydrates: 5-10% of total daily calories
These ratios may vary based on individual goals, such as weight loss, muscle gain, or managing medical conditions.
2. Foods to Eat
On the keto diet, focus on consuming the following foods:
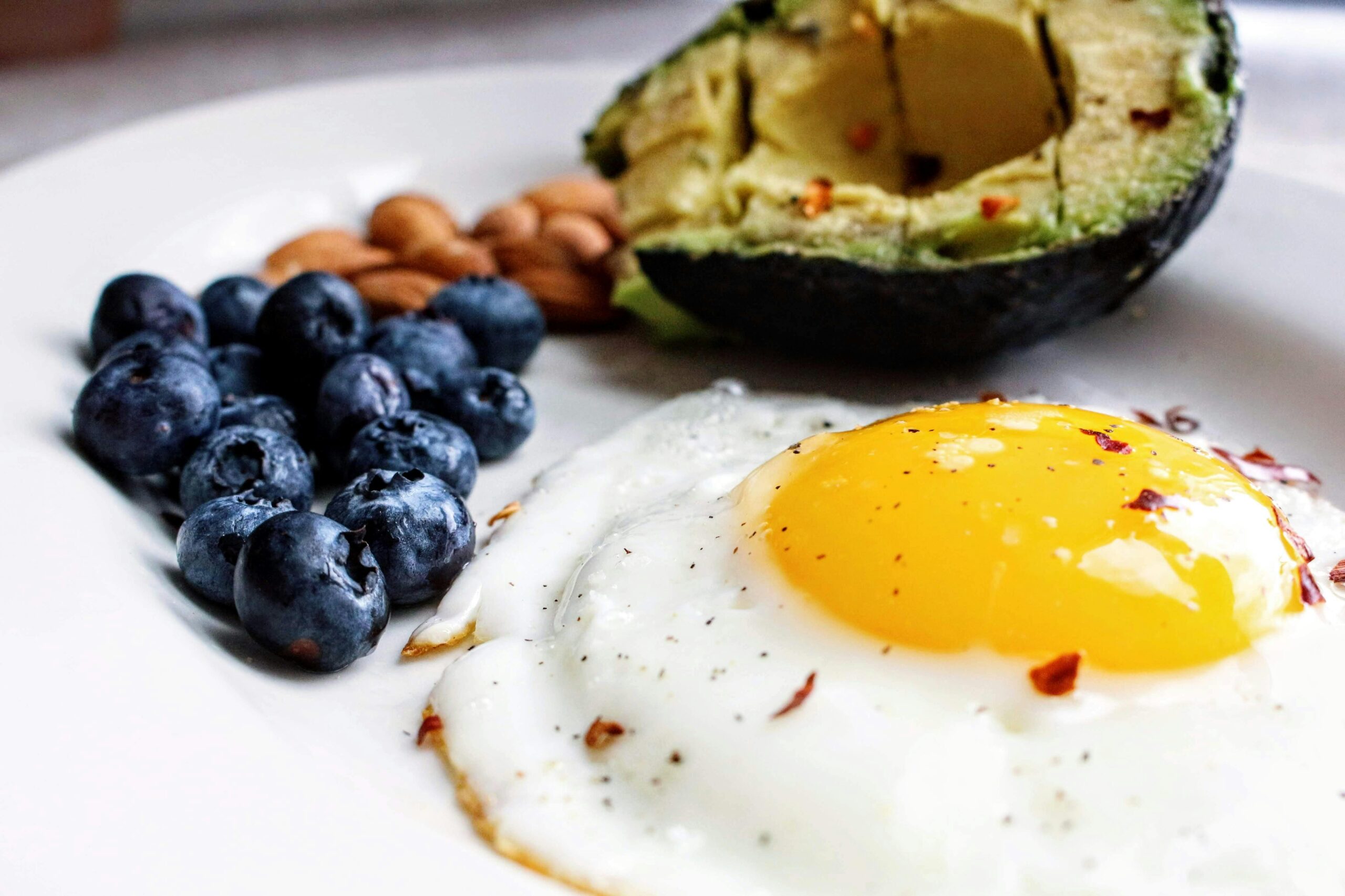
- Healthy fats: Avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, nuts, and seeds
- Protein: Meat, fish, eggs, and low-carb dairy products
- Low-carb vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, and bell peppers
- Berries: Strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries in moderation
3. Foods to Avoid
Certain foods should be limited or avoided on the keto diet:
- High-carb foods: Bread, pasta, rice, and sugary snacks
- Starchy vegetables: Potatoes, corn, and peas
- Fruits: Most fruits, except for small portions of berries
- Sugary beverages: Soda, juice, and sweetened coffee drinks
Benefits of the Keto Diet
The keto diet offers several potential benefits, making it an attractive option for many individuals:
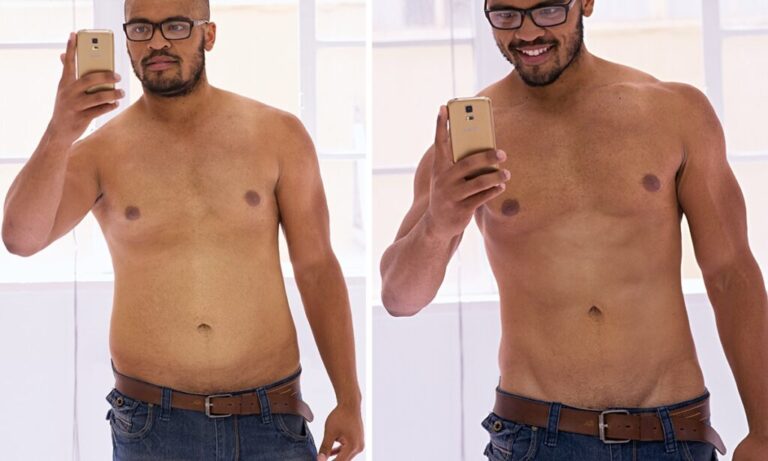
1. Weight Loss
One of the primary reasons people choose the keto diet is for weight loss. By limiting carbohydrate intake, the body shifts its focus to burning fat for energy, leading to a reduction in body fat. Additionally, the high-fat content of the diet can promote satiety, reducing overall calorie intake.
2. Improved Mental Clarity
Many individuals report increased mental clarity and focus when following the keto diet. Ketones, produced during ketosis, are a more efficient fuel source for the brain than glucose, which may contribute to improved cognitive function.
3. Enhanced Energy Levels
Once the body adapts to burning fat for fuel, many people experience stable energy levels throughout the day. Unlike the energy crashes associated with high-carb diets, keto can provide consistent energy without the need for frequent meals or snacks.
4. Blood Sugar Control
The keto diet may help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. By reducing carbohydrate intake, individuals may experience fewer blood sugar spikes and crashes, making it beneficial for those with diabetes or prediabetes.
5. Potential Health Benefits
Emerging research suggests that the keto diet may have therapeutic benefits for various health conditions, including:
- Epilepsy: Originally developed to manage epilepsy in children, the keto diet has shown effectiveness in reducing seizure frequency.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Some studies indicate that ketosis may provide neuroprotective effects, potentially benefiting conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): The diet may help regulate hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While the keto diet can be beneficial for many individuals, it is essential to consider potential risks and challenges:
1. Nutrient Deficiencies
Restricting carbohydrate intake may lead to deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals. It is crucial to ensure a well-rounded diet by incorporating low-carb vegetables and supplements if necessary.
2. Keto Flu
Some individuals may experience flu-like symptoms during the initial transition to ketosis, commonly referred to as “keto flu.” Symptoms can include fatigue, headaches, irritability, and digestive issues. Staying hydrated and gradually reducing carbs can help mitigate these effects.
3. Digestive Issues
Changes in diet may lead to digestive issues, such as constipation or diarrhea. Including fiber-rich, low-carb foods and staying hydrated can help promote healthy digestion.
4. Long-Term Sustainability
The restrictive nature of the keto diet may make it challenging to maintain over the long term. It’s essential to find a balance that works for you and consider cycling in and out of the diet as needed.
5. Medical Considerations
Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as liver or pancreatic disorders, should consult with a healthcare professional before starting the keto diet. It is also essential to monitor any potential side effects while following the diet.
Meal Planning for the Keto Diet
Successful adherence to the keto diet often involves careful meal planning. Here are some tips to help you get started:
1. Create a Meal Plan
Plan your meals for the week ahead, focusing on keto-friendly ingredients. Include a variety of proteins, healthy fats, and low-carb vegetables to ensure balanced nutrition.
2. Keep Snacks on Hand
Having keto-friendly snacks readily available can help prevent cravings and keep you on track. Some great options include:
- Nuts and seeds
- Cheese
- Hard-boiled eggs
- Veggies with guacamole or ranch dressing
3. Batch Cooking
Prepare larger quantities of keto-friendly meals and store them in the fridge or freezer for easy access during busy days. This practice can help save time and ensure you have healthy options available.
4. Use Keto Recipes
Explore various keto recipes to keep your meals exciting and flavorful. Many online resources and cookbooks provide delicious meal ideas that align with the keto diet.
Tips for Success on the Keto Diet
To make the most of your keto journey, consider the following tips:
1. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential, especially when transitioning to the keto diet. Increased water intake can help prevent the “keto flu” and support overall health.
2. Monitor Your Macros
Consider using a tracking app to monitor your daily macronutrient intake. This practice can help you stay within your target ratios and make adjustments as needed.
3. Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to how your body responds to the keto diet. If you experience adverse effects or feel unwell, it may be worth reassessing your approach or consulting with a healthcare professional.
4. Be Patient
Achieving ketosis and experiencing the full benefits of the diet may take time. Be patient with yourself during the transition, and give your body the time it needs to adjust.
5. Seek Support
Joining a keto community or finding a support group can help you stay motivated and share tips with others on a similar journey.
Conclusion
The keto diet offers a unique approach to nutrition that can promote weight loss, improved energy levels, and various health benefits. By understanding its principles and focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods, individuals can successfully navigate the challenges of this low-carb, high-fat lifestyle. While the diet may not be suitable for everyone, it has shown promising results for many. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes, and remember that the best diet is one that is sustainable and aligns with your individual health goals.