Stevia, a popular natural sweetener derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, has gained significant attention in recent years as a healthier alternative to sugar and artificial sweeteners. As consumers increasingly seek low-calorie options for sweetening their food and beverages, questions about the safety of stevia, particularly regarding its potential link to cancer, have become more prevalent. In this article, we will explore the question: does stevia cause cancer? We will delve into the science behind stevia, examine its health effects, and discuss any existing research on its safety.
Understanding Stevia
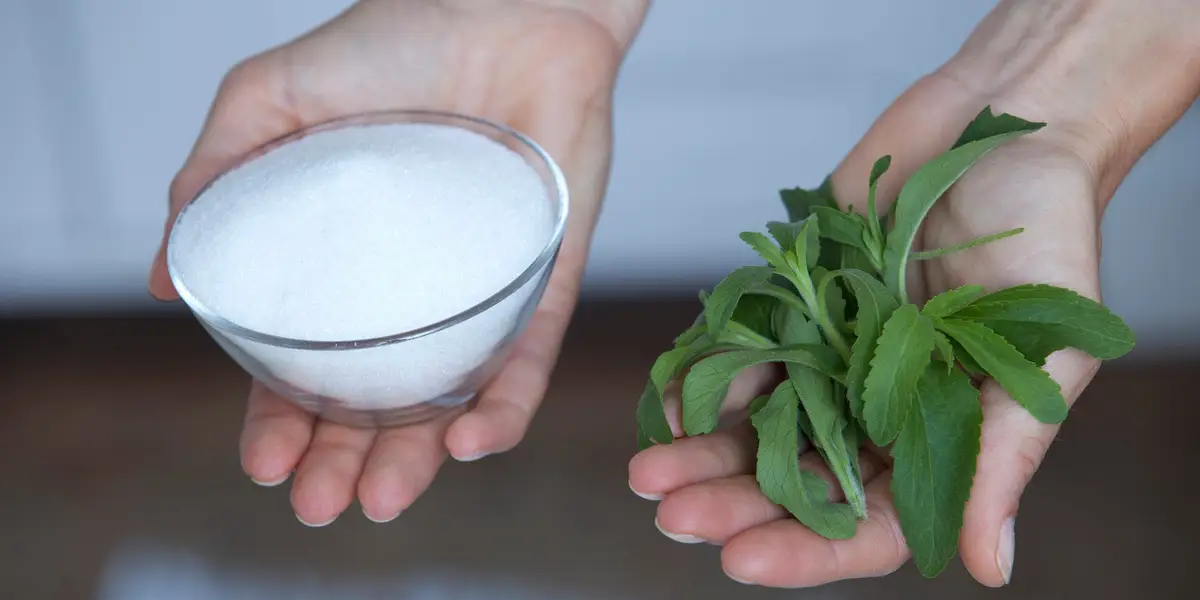
What is Stevia?
Stevia is a natural sweetener extracted from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, native to South America. The sweet compounds in stevia, called steviol glycosides, are estimated to be 50 to 300 times sweeter than sucrose (table sugar), making it a potent sugar substitute. Because stevia contains minimal calories, it has become a popular choice for those looking to reduce sugar intake and manage weight.
How is Stevia Processed?
The processing of stevia involves several steps:
- Harvesting: The leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant are harvested.
- Extraction: The sweet compounds are extracted from the leaves using water or alcohol.
- Purification: The extracted solution undergoes purification to isolate the steviol glycosides.
- Drying and Powdering: The purified extract is then dried and powdered to create the stevia sweetener that consumers find in stores.
Common Forms of Stevia
Stevia is available in various forms, including:
- Liquid Drops: Concentrated liquid extracts used for sweetening drinks and foods.
- Powdered Stevia: Dry, powdered form that can be used in baking or as a tabletop sweetener.
- Stevia Blends: Mixtures of stevia with other sweeteners or fillers, often found in commercial products.
The Rise of Stevia as a Sweetener
Popularity and Use
Stevia has gained popularity not only for its sweetness but also for its perceived health benefits. It is often marketed as a natural, zero-calorie alternative to sugar, making it appealing to those with diabetes, individuals seeking to lose weight, and those looking to reduce sugar consumption.
Consumer Concerns
Despite its popularity, concerns about the safety of stevia have arisen, particularly regarding its long-term health effects. One of the most pressing questions is whether stevia has any carcinogenic properties.
Does Stevia Cause Cancer? The Research
Overview of Carcinogenicity
Carcinogenicity refers to the ability of a substance to promote cancer formation. When assessing whether a sweetener like stevia could be carcinogenic, researchers consider several factors:
- Chemical Composition: The chemical structure of steviol glycosides and their metabolic products.
- Animal Studies: Research on the effects of stevia on laboratory animals.
- Human Studies: Epidemiological studies examining the long-term health effects of stevia consumption in humans.
Studies on Stevia and Cancer
Animal Studies
Several animal studies have been conducted to assess the potential carcinogenic effects of stevia:
- Study by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): A review of available data indicated that steviol glycosides were not associated with an increased risk of cancer in animal models.
- Research on Long-Term Exposure: In a long-term study involving rats, researchers found no evidence that stevia consumption led to cancer development or any adverse health effects.
Human Studies
Human studies on stevia’s potential link to cancer are limited. However, some research has provided insights:
- Epidemiological Studies: Most observational studies have not found a significant association between stevia consumption and cancer incidence.
- Case-Control Studies: Some studies have suggested that individuals who use stevia as a sweetener do not exhibit higher rates of specific cancers compared to non-users.
Regulatory Perspectives
Approval and Safety Assessments
Stevia has been evaluated by various regulatory bodies around the world:
- FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration): In 2008, the FDA granted GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status to highly purified steviol glycosides. This means they are considered safe for consumption based on available scientific evidence.
- EFSA: The EFSA conducted comprehensive assessments and concluded that steviol glycosides do not pose a cancer risk to consumers.
Conclusion from Research
The current body of research suggests that stevia does not cause cancer. Both animal and human studies indicate that stevia consumption is safe and does not increase cancer risk. However, ongoing research is essential to monitor long-term effects and any potential risks.
Potential Health Benefits of Stevia
Zero-Calorie Sweetener
One of the primary advantages of stevia is its zero-calorie content. For those looking to manage weight or reduce calorie intake, stevia can be an effective alternative to sugar.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Stevia has been studied for its potential effects on blood sugar levels:
- Diabetes Management: Some research suggests that stevia may help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, making it a suitable sweetener for people with diabetes.
Antioxidant Properties
Stevia contains various antioxidants, which can help combat oxidative stress in the body. Antioxidants are known to play a role in reducing inflammation and supporting overall health.
Possible Side Effects of Stevia
Digestive Issues
Some individuals may experience digestive discomfort when consuming stevia, particularly in larger quantities. Common side effects include:
- Bloating
- Gas
- Nausea
Allergic Reactions
Although rare, some people may be allergic to stevia or its components. Symptoms can include:
- Skin rashes
- Itching
- Difficulty breathing
Taste Preference
Not everyone enjoys the taste of stevia. Some people may find it has a bitter aftertaste, which can affect their willingness to use it as a sugar substitute.
Alternatives to Stevia
Other Natural Sweeteners
If you’re looking for alternatives to stevia, several natural sweeteners are available:
- Honey: A natural sweetener with a distinct flavor and potential health benefits.
- Agave Nectar: A sweetener derived from the agave plant, often used in vegan diets.
- Monk Fruit Extract: Another natural sweetener that has gained popularity for its sweetness and low-calorie content.
Artificial Sweeteners
For those open to artificial options, several sweeteners are widely used:
- Aspartame: A low-calorie sweetener commonly found in diet sodas.
- Sucralose: A calorie-free sweetener often used in baked goods and beverages.
How to Use Stevia in Your Diet
Cooking and Baking with Stevia
When using stevia in cooking or baking, consider the following tips:
- Measurement: Since stevia is much sweeter than sugar, use it sparingly. Refer to the package for conversion ratios.
- Combining with Other Ingredients: Mixing stevia with other sweeteners or ingredients can enhance flavor and texture.
- Baking Adjustments: Stevia can be used in baking, but moisture levels may need adjustment since it lacks the bulk of sugar.
Incorporating Stevia into Beverages
Stevia can be added to a variety of beverages:
- Tea and Coffee: A few drops or a sprinkle of powdered stevia can sweeten your favorite hot or cold drinks.
- Smoothies: Add stevia to smoothies for a naturally sweet taste without extra calories.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is stevia safe for everyone?
Yes, stevia is generally considered safe for most people, including those with diabetes. However, individuals with specific allergies or digestive sensitivities should monitor their intake.
2. Can stevia be used in cooking?
Absolutely! Stevia can be used in a variety of cooking and baking recipes. Just remember to adjust the amount since it is much sweeter than sugar.
3. Does stevia affect blood sugar levels?
Stevia is not expected to raise blood sugar levels, making it a suitable sweetener for individuals with diabetes or those managing their blood sugar.
4. What are the side effects of stevia?
While stevia is safe for most, some individuals may experience digestive discomfort or allergic reactions. It’s best to start with small amounts to assess tolerance.
5. Are there any long-term studies on stevia?
Ongoing research continues to examine the long-term effects of stevia consumption. Currently, the available studies suggest it is safe and does not cause cancer.
Conclusion
In summary, the question does stevia cause cancer? is met with a reassuring answer based on current scientific research. The evidence indicates that stevia is safe for consumption and does not pose a cancer risk. As with any dietary choice, moderation is key, and it’s essential to consider individual health needs and preferences. Stevia offers a natural, calorie-free way to sweeten foods and beverages while supporting overall health goals. As research continues to evolve, consumers can feel confident in enjoying stevia as part of a balanced diet.